Understand RBAC and privileges
ThoughtSpot Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) helps an administrator manage roles and privileges that are assigned to users and groups in ThoughtSpot. A role is a collection of privileges. A privilege allows users to perform certain actions while preventing them from performing other actions. RBAC enhances the granularity of permissions that determine the access and capabilities of users and admins.
Roles can be assigned to groups. A group can have one or more roles assigned to it. When multiple roles are assigned to a group, the privileges available to users within that group are a union of the privileges in each role assigned to the group.
RBAC is disabled by default. To enable this feature, contact ThoughtSpot support.
| Once you enable RBAC it cannot be disabled. |
Roles and privileges
A role is a collection of privileges. The role and its assigned privileges list the actions that can be performed, such as Can administer ThoughtSpot or Can upload user data. Roles can be high-level, like Super Admin, or specific based on your organization’s structure and requirements. Roles are configured and then assigned to groups.
ThoughtSpot delivers some standard roles to help you transition to RBAC.
With RBAC is enabled on your instance, administrators can grant granular privileges to implement fine-grained access control to ThoughtSpot features, objects, and metadata. For example, on ThoughtSpot instances without RBAC enabled, members of the groups with administration privileges can view and administer users, groups, and roles. With RBAC enabled, you can assign granular privileges and restrict application-wide access only to super admin users.
| ThoughtSpot privilege (without RBAC enabled) | ThoughtSpot RBAC roles |
|---|---|
Can administer ThoughtSpot Grants administration permissions to manage users and groups on instances that do not have the RBAC feature enabled. |
RBAC allows multiple roles with granular privileges for administration control User administration: Can manage Users Group administration: Can manage Groups Role administrator: Can manage Roles Org administration: Can manage Orgs Authentication administration: Can manage Authentication Application administration: Can manage Application settings |
Previously, administrators were part of the administrator group, and data mangers were part of the can manage data group. Members of the groups would have view and edit access to all data. In some organizations these functions are broken out in a more granular way between different users. Roles allow you to assign the specific roles and privileges required without including those that are not needed.
| ThoughtSpot RBAC includes a Super Admin role that includes all of the privileges previously included in the Administrator group to help you migrate to RBAC. Users with this privilege can access all cluster data. This privilege should only be granted in exceptional circumstances. |
Understanding Role Assignment (Without RBAC Roles)
Administrators can create a role with a specific set of privileges and assign this role to a group. Users inherit role privileges from the groups to which they are assigned. To assign a role to a user, administrators must assign the role to a group and ensure that the intended users are added to this group. The following figure illustrates the role and group assignment in ThoughtSpot:
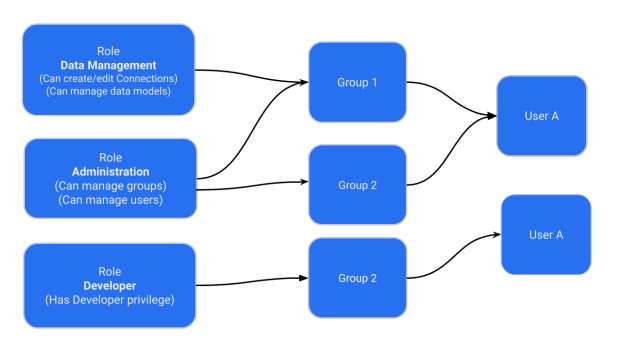
| Roles are unique to an Org and can be created only within the context of an Org. |
RBAC roles
The following are descriptions of each of the RBAC roles.
Administrative privileges
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
Can manage Orgs |
Applicable to ThoughtSpot instances with Orgs. User with Can manage Orgs can create and manage objects, groups and users in their respective Orgs. NOTE: Without RBAC enabled, Can manage Orgs has super admin privileges. With RBAC enabled, this role gives privilege only to perform CRUD operations on Orgs. |
Can manage Users |
Allows administrators and users to create, view, update and delete users. |
Can manage Groups |
Allows administrators and users to create, view, update and delete groups. |
Can manage Roles |
Allows administrators and users to create, view, update and delete roles. |
Can manage Authentication |
Allows administrators and users to manage authentication and the authorization process for ThoughtSpot users. |
Can manage Application settings |
Allows administrators and users to manage cluster-wide application settings, activation and de-activation of feature on an instance. |
Can view System activities |
Allows administrators and users to manage system activities. |
Can view Billing Information |
Allows view access to billing information. |
Can Enable or Disable Trusted Authentication |
Allows users with Super Admin privilege to enable or disable trusted authentication for applications embedding ThoughtSpot content. |
Can manage tags |
Allows administrators and users to create and edit tags. |
Can manage Analyst Studio |
Allows administrators and users to manage Analyst Studio for ThoughtSpot users. |
Object access control privileges
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
Can share with all users |
Allows users to share objects with all the users and groups in ThoughtSpot. |
Data control privileges
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
Can create/edit connections |
Allows administrators and users to add new data connections or edit existing connections to external data warehouses. |
Can manage data models |
Allows users to create, edit, delete and manage Models, Tables, and Views. |
Can manage custom calendars |
Allows users to create, edit, or delete custom calendars. |
Can upload user data |
Allows users to upload data to ThoughtSpot. |
Can administer and bypass RLS |
Allows access to the following operations:
For more information, see Row-level security. |
Application control privileges
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
Has SpotIQ privilege |
Allows access to the SpotIQ feature in ThoughtSpot. |
Has developer privilege |
Allows users to access the following features and workflows:
|
Can schedule for others |
Allows users to schedule, edit, and delete Liveboard jobs. |
Can Manage Sync settings |
Allows for set up of secure pipelines to external business apps and syncing of data using ThoughtSpot Sync. |
Can use Spotter |
Allows access to ThoughtSpot Spotter features. |
Can manage catalog |
Allows users to create, edit, and mange a data connection to Alation, and import metadata. |
Can invoke Custom R Analysis |
Allows invoking R scripts to explore search answers and share custom scripts. |
Can verify Liveboard |
Allows Liveboard users to verify Liveboard access requests and mark a Liveboard as verified. |
Can use Analyst Studio |
Allows access to Analyst Studio features. |
Can manage version control |
Allows users to connect Git branches to ThoughtSpot for version control. |
Migrating to RBAC
ThoughtSpot delivers roles corresponding to each privilege previously available as part of the existing groups. Existing groups are retained. When migrating, for each existing group privilege, a new role is created with the corresponding privileges assigned, and the existing groups are mapped to the corresponding new role.
For example, where an existing cluster has a group GroupA with privilege Has Developer Privilege, when RBAC is enabled, a role wis created _Developer that has all granular privileges representing Has Developer Privilege assigned and GroupA has the _Developer role assigned.
The following image shows how Groups appear in the UI:
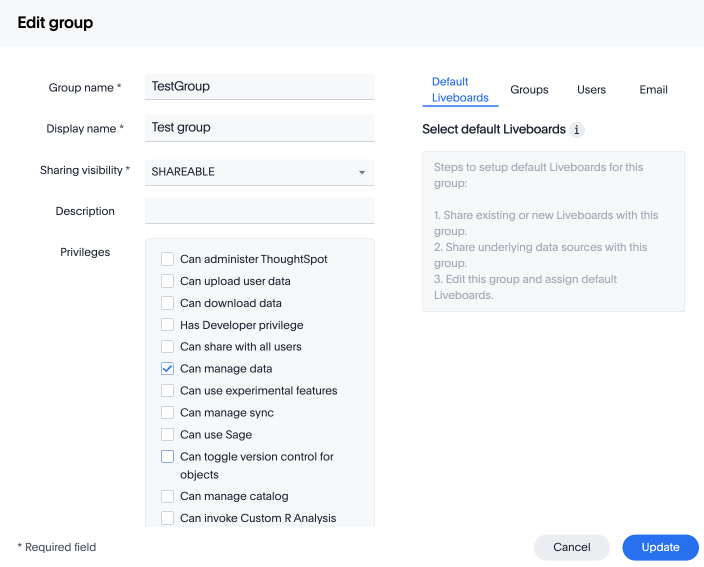
Without RBAC enabled, you will see the following privileges:
With RBAC enabled, you will see the following privileges:
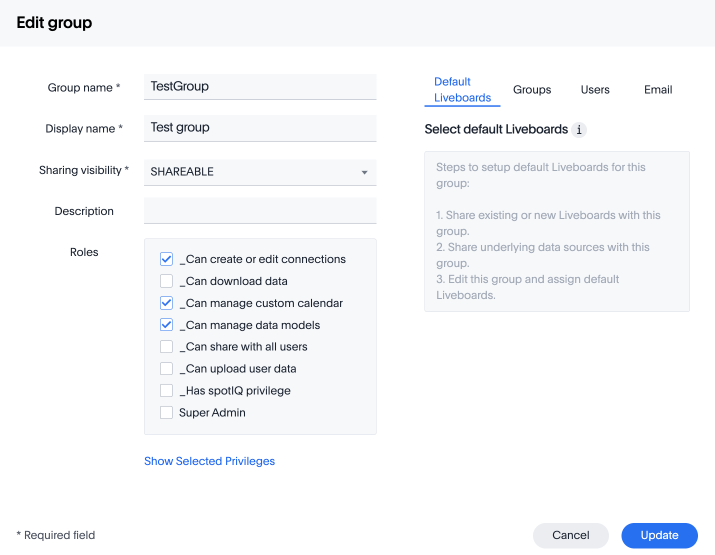
| There are no changes made to the existing privileges. Existing privileges are mapped to roles which are assigned to the new granular privileges which make up the old monolithic privilege. |
Create, edit, or delete a role
ThoughtSpot has customizable RBAC management for assigning privileges to roles. Before adding users to groups, you can create custom roles if necessary and assign them to groups. Each role includes a set of privileges for its users.
Create a role
To create a role, follow these steps:
-
Select Admin settings from your profile menu.
-
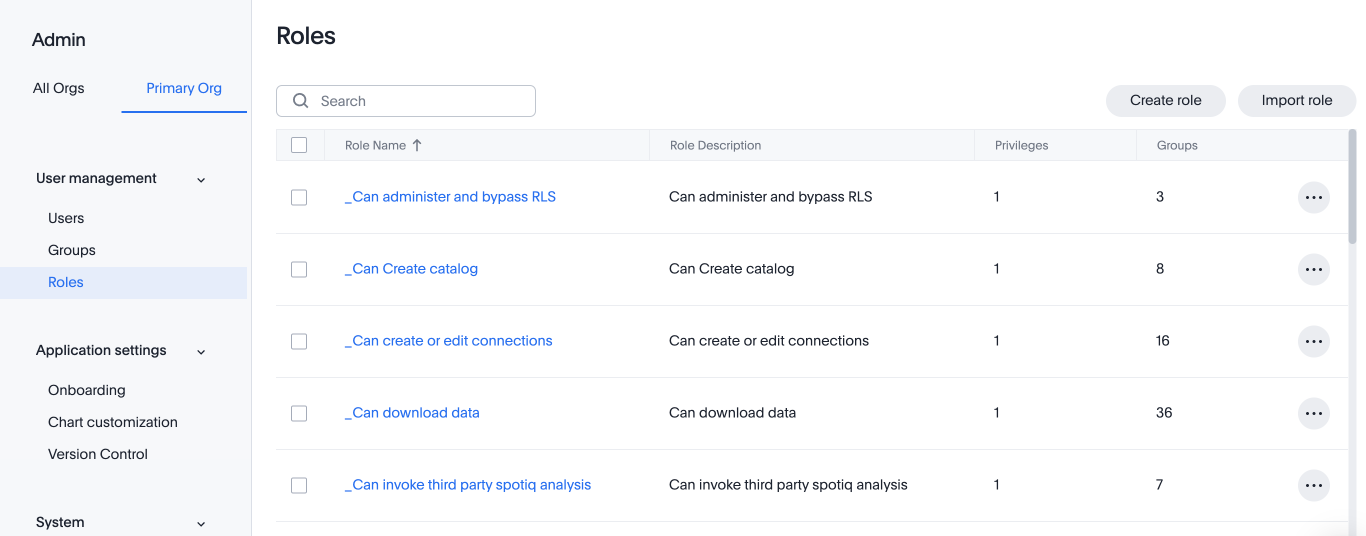
Select Roles from the User management section in the side navigation bar.
-
Select the Create role button on the right side of the screen.
-
In the Create role modal, enter the details for the new role:
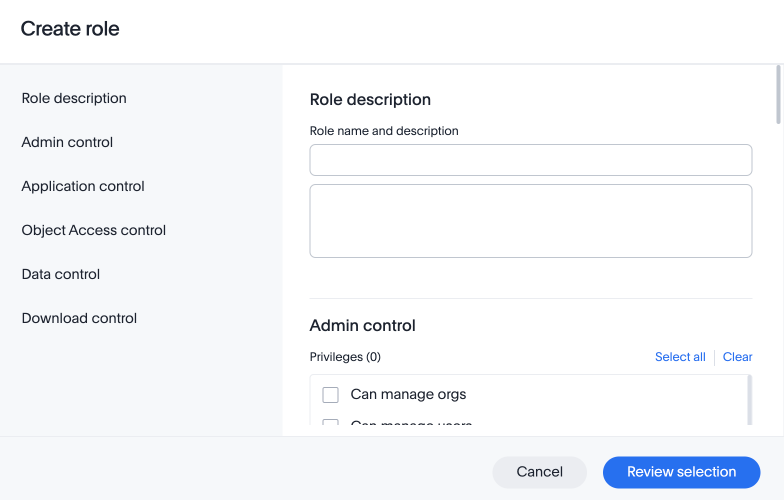
- Role name
-
Enter a unique name for the role.
- Role description
-
Optionally, enter a description.
- Privileges
-
Check the privileges you want to grant to the role.
The granular privileges provided by ThoughtSpot are grouped. For example privileges related to data management are grouped under Data Control. The controls and associated privileges are listed in the modal. Users can either scroll down to access each one, or click on the relevant section title on the left side to access the desired group and associated privileges.
-
Click Review selection to continue.
-
Review your selections, and click Save to create the new role.
If you give a new role a role name which is the same as that of an existing role, you will see and error about the duplication of role with a suggestion to change the role name when you click Save. 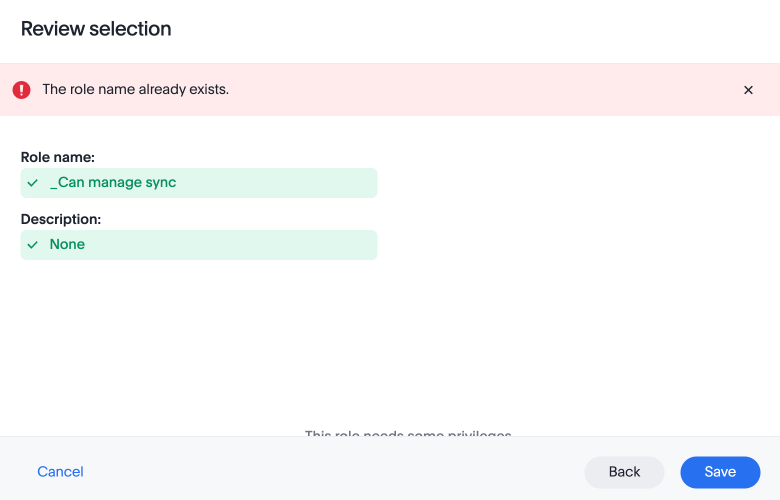
Edit a role
To edit a role, follow these steps:
-
Select Admin settings from your profile menu.
-
Select Roles from the User management section in the side navigation bar.

-
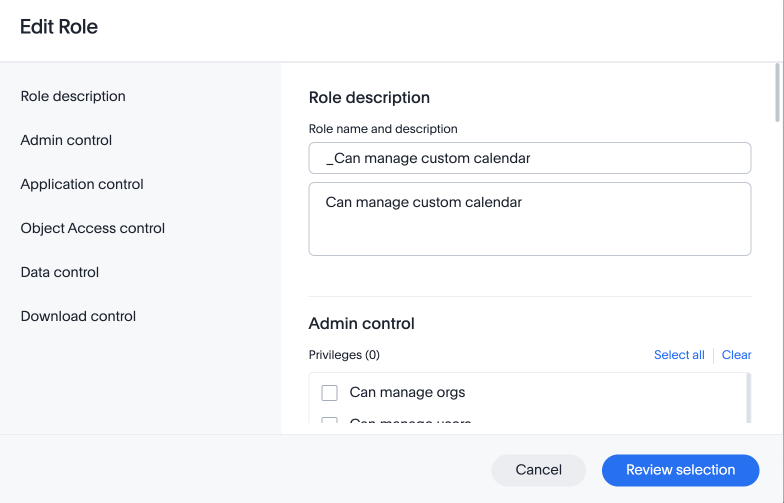
Click on a role name, or click More options and select Edit to edit the role.
-
In the Edit role modal, make your desired changes.
-
Click Review selection to continue.
-
Review your changes, and click Save.
Delete a role
To delete a role, follow these steps:
-
Select Admin settings from your profile menu.
-
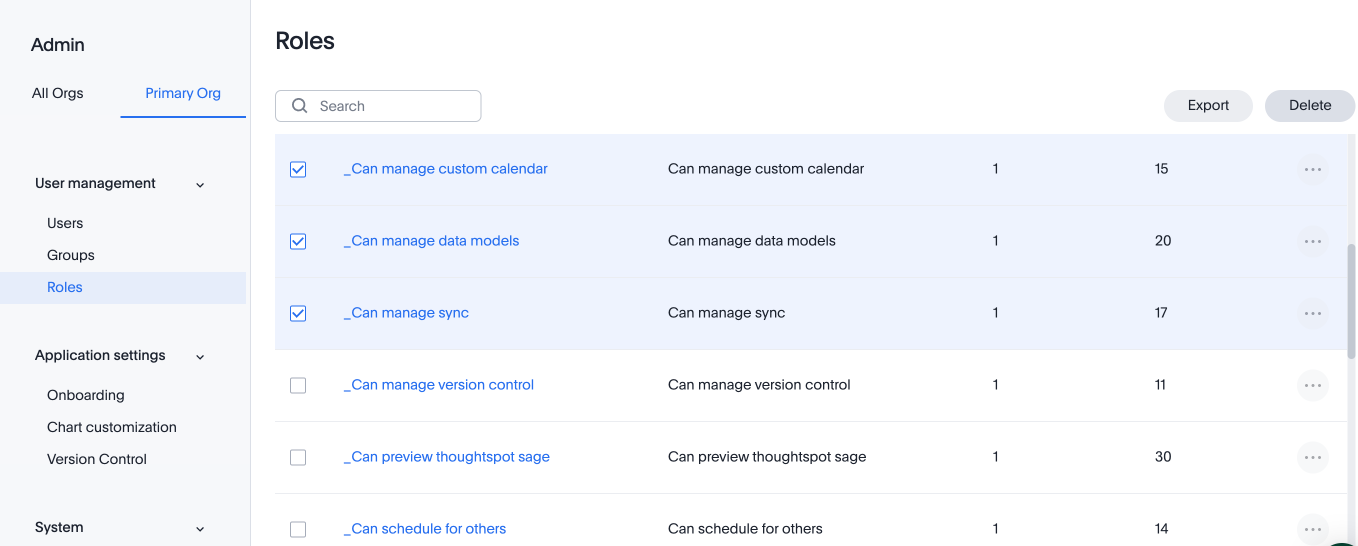
Select Roles from the User management section in the side navigation bar.

-
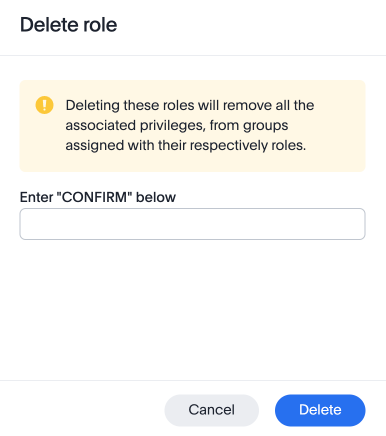
To delete multiple roles at the same time, select the checkboxes next to the role names and click the Delete button.
-
Type CONFIRM and click Delete to delete.
Assign roles to groups
Once you have created roles, you can assign them to groups to manage privileges for your users. For more information about assigning roles to groups, see Understand groups and privileges Create, edit, or delete a group.




