Configure trusted authentication
Learn how to configure trusted authentication.
If your organization has a trusted authentication server, you can use it to authenticate users of the embedded ThoughtSpot application. After authenticating a user, the trusted authenticator server or service obtains an authentication token from ThoughtSpot on that user’s behalf. This ensures that the user authentication persists across all subsequent user sessions.
How to authenticate users
In the following scenario, the trust authenticator forwards requests for ThoughtSpot data from client applications.
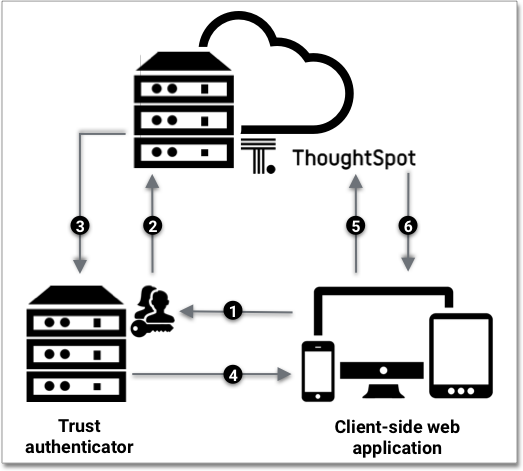
A user already logged into the client application interacts with a ThoughtSpot embed point, which launches the following sequence:
-
The client-side application requests a user token from the trusted authenticator.
This trusted authenticator server must already be configured as an authenticated server.
-
The trusted server authenticates the user, and requests a token from ThoughtSpot on the user’s behalf.
-
ThoughtSpot verifies the authenticator server’s request and returns a user token.
-
The authenticator returns the user token to the client, which it uses to complete the user request.
-
The client forwards the request and the user token to ThoughtSpot.
-
ThoughtSpot validates the token, and returns the information that the authenticated user requested.
Enable trusted authentication and get a token
Generated tokens do not expire.
-
Log in to the ThoughtSpot server.
-
Enable trusted authentication and generate an authenticate token. (service secret) — used to identify the server to ThoughtSpot.
[admin@ourthoughtspot ~]$ tscli tokenauthentication enable Token generated. Copy the GUID in the box. ######################################## # b0cb26a0-351e-40b4-9e42-00fa2265d50c # ######################################## Override added successfully
Tokens are like any other password. You should store them securely and protect knowledge of them. Your installation can have only one authentication token at a time. Every time you call to enable overwrite, the existing token and return a new one.
Disable a token
To disable a token and not overwrite it, enter the following command:
tscli tokenauthentication disable
Trusted authentication call
-
A user in another application or web page requests access to embedded ThoughtSpot.
This is a REST request for an embedded ThoughtSpot object, page, or entire application. Your trusted authenticator server intercepts the request. Your server application must determine, at minimum:
-
if the requestor is itself authenticated with your server
-
which user (
username) is making the request -
what is being requested: an object, page, or the entire ThoughtSpot application
It is also important that the
usernameis a match for ausernameon the ThoughtSpot application. -
-
The trusted web server requests an authentication token on the user’s behalf from ThoughtSpot.
POST https://<instance>/callosum/v1/session/auth/token
This post request takes the following parameters:
- secret_key
-
A required
formDataparameter containing a string which is the authentication token provide by the ThoughtSpot server. - username
-
A required
formDataparameter containing a string which is the user’susernameon ThoughtSpot. - access_level
-
A required
formDataparameter containing one ofFULLorREPORT_BOOK_VIEW. - id
-
An optional
formDataparameter containing a ThoughtSpot object identifier. This is only required if you specifiedREPORT_BOOK_VIEWfor theaccess_levelparameter.
-
The trusted authenticator server is responsible for managing this token.
The token can be managed in any way you see fit. Tokens expire in XXX minutes/hours/day.
-
The trusted authenticator server returns a token to the original requestor.
-
Client completes the user’s request, providing the token along with the request.
For example, the customer requests a specific object:
GET https://<instance>/callosum/v1/session/login/token?username=<user>&auth_token=<token>&redirect_url=<full-encoded-url-with-auth-token>
If you are using ThoughtSpot embed with objects or pages, you must request re-authenticate requests for each new object.



