Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp
SpotApps are ThoughtSpot’s out-of-the-box solution templates built for specific use cases and data sources. They are built on ThoughtSpot Modeling Language (TML) Blocks, which are pre-built pieces of code that are easy to download and implement directly from the product.
The Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp mimics the Redshift data model. When you deploy it, ThoughtSpot creates several Worksheets, Answers, and Liveboards, based on your Redshift data in your cloud data warehouse.
This is a sample Liveboard, created after you deploy the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp:
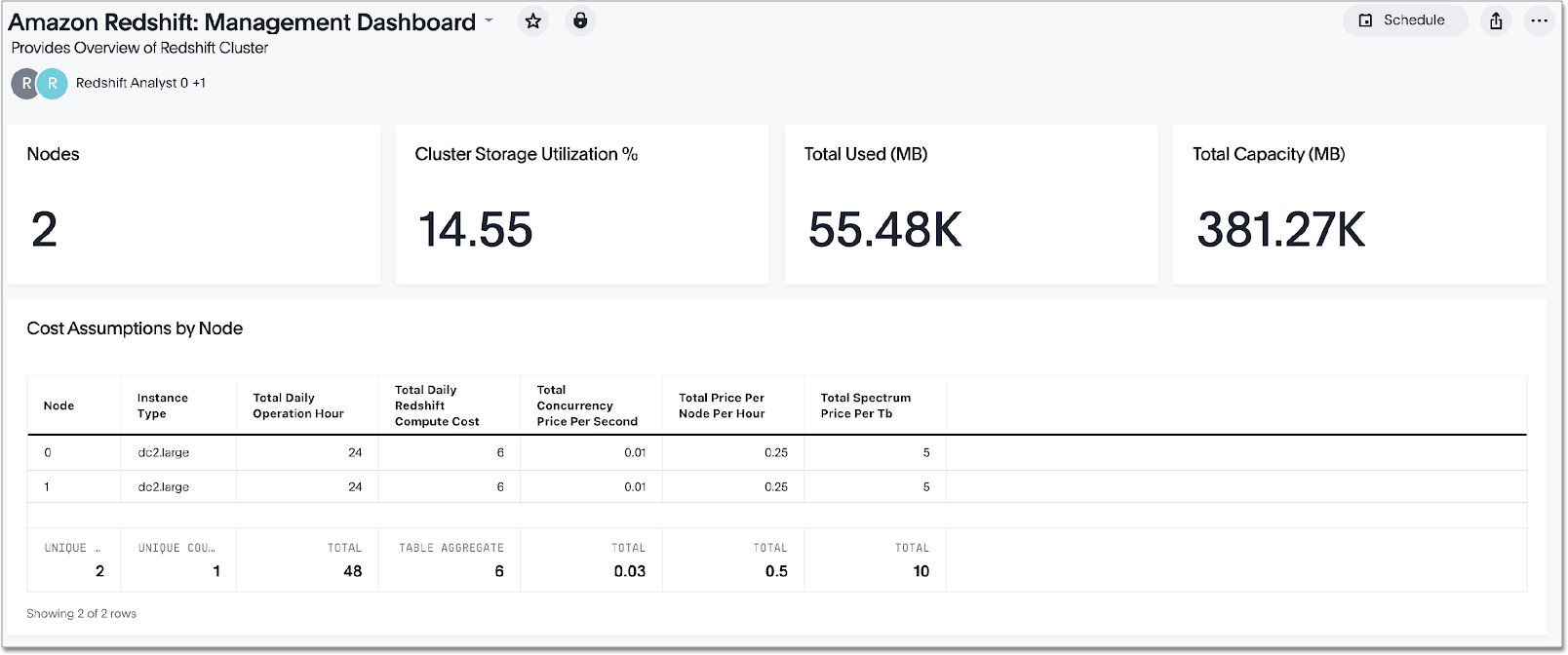
Use the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp to manage costs and investigate query performance. Track how and where your users consume credits, and triage and resolve any performance bottlenecks.
Prerequisites
Before you can deploy the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp, you must complete the following prerequisites:
-
Review the required tables and columns for the SpotApp.
-
Ensure that your columns match the required column type listed in the schema for your SpotApp.
-
Sync all tables and columns from Redshift to your cloud data warehouse. You can sync only the required tables and columns, but ThoughtSpot recommends syncing all tables and columns from Redshift to your CDW. The columns can be Redshift’s out-of-the-box columns, or any custom columns that you are using instead of the out-of-the-box columns.
If you are using an ETL/ELT tool or working with another team in your organization to move data, our recommendation is that you sync all columns from the tables listed in the SpotApp. -
Obtain credentials and SYSADMIN privileges to connect to Redshift. The cloud data warehouse must contain the data you would like ThoughtSpot to use to create Answers, Liveboards, and Worksheets. Refer to the Connection reference for Redshift for information about required credentials.
-
The connection name for each new SpotApp must be unique.
-
Administrator access to Redshift
-
You must create views based on the following Redshift tables in your cloud data warehouse. If you already created the views, you only need access to the views, not the tables. Refer to Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp schema for more details.
-
pg_user
-
stl_query
-
stl_wlm_query
-
stv_wlm_service_class_config
-
svl_qlog
-
stl_alert_event_log
-
svv_table_info
-
stv_sessions
-
stl_load_errors
-
stv_node_storage_capacity
-
stl_ddltext
-
stl_plan_info
-
svl_query_metrics_summary
-
svl_s3query_summary
-
-
Access to the following Redshift views in your cloud data warehouse:
-
pg_user_vw
-
stl_query_vw
-
stl_wlm_query_vw
-
stv_wlm_service_class_config_vw
-
svl_qlog_vw
-
stl_alert_event_log_vw
-
svv_table_info_vw
-
stv_sessions_vw
-
stl_load_errors_vw
-
stv_node_storage_capacity_vw
-
stl_ddltext_vw
-
stl_plan_info_vw
-
svl_query_metrics_summary_vw
-
svl_s3query_summary_vw
-
-
Run the required SQL commands in your cloud data warehouse. Refer to Run SQL commands.
Run SQL commands
The following SQL commands create the required views based on the required tables.
| The following SQL example is for the Redshift cloud data warehouse. You may need to modify the code for the SQL requirements of your specific cloud data warehouse. |
SQL commands:
Open the dropdown menu to view the SQL commands.
create view dev.public.pg_user_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.pg_user;
create view dev.public.stl_alert_event_log_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stl_alert_event_log;
create view dev.public.stl_ddltext_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stl_ddltext;
create view dev.public.stl_load_errors_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stl_load_errors;
create view dev.public.stl_plan_info_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stl_plan_info;
create view dev.public.stl_query_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stl_query;
create view dev.public.stl_wlm_query_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stl_wlm_query;
create view dev.public.stv_node_storage_capacity_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stv_node_storage_capacity;
create view dev.public.stv_sessions_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stv_sessions;
create view dev.public.stv_wlm_service_class_config_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.stv_wlm_service_class_config;
create view dev.public.svl_qlog_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.svl_qlog;
create view dev.public.svl_query_metrics_summary_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.svl_query_metrics_summary;
create view dev.public.svl_s3query_summary_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.svl_s3query_summary;
create view dev.public.svv_table_info_vw as select * from dev.pg_catalog.svv_table_info;Deploy the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp
After you complete the prerequisites, you are ready to deploy the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp and begin leveraging its pre-built content.
To deploy the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp, refer to Deploying SpotApps.
Review formula values
After you deploy the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp, you must review the default formula values ThoughtSpot used in several formulas in the Amazon Redshift Clusters Worksheet. Your values may be different from the default values ThoughtSpot used in the formulas. To ensure the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp is as useful for your specific data as possible, review the values in the following formulas in the Amazon Redshift Clusters Worksheet.
All currency values are in USD. If necessary, convert them to your currency.
-
instance type: By default, this is set todc2.large. If necessary, replace this value with the node/instance type for your Redshift cluster and region. -
Price Per Node Per Hour (Currency): If necessary, replace this value with the value for your node type and region. Refer to "On-demand pricing" in the Redshift pricing documentation. -
Spectrum Price Per TB (Currency): If necessary, replace this value with the value for your region. Refer to "Amazon Redshift Spectrum pricing" in the Redshift pricing documentation. -
Concurrency Price per Second (Currency): If necessary, replace this value with the value for your region. Refer to "Concurrency Scaling Pricing" in the Redshift pricing documentation.
Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp schema
The following table describes the schema for the Redshift Performance and Consumption SpotApp.
| Table/View | Column | Column type | Required column |
|---|---|---|---|
pg_user_vw |
usename |
varchar |
Y |
pg_user_vw |
usesuper |
bool |
N |
pg_user_vw |
usesysid |
int |
Y |
stl_query_vw |
query |
int |
Y |
stl_query_vw |
pid |
int |
Y |
stl_query_vw |
database |
varchar |
Y |
stl_query_vw |
querytxt |
varchar |
Y |
stl_query_vw |
starttime |
timestamp |
N |
stl_query_vw |
endtime |
timestamp |
N |
stl_query_vw |
aborted |
int |
N |
stl_query_vw |
userid |
int |
N |
stl_wlm_query_vw |
query |
int |
Y |
stl_wlm_query_vw |
service_class |
int |
Y |
stv_wlm_service_class_config_vw |
name |
varchar |
Y |
stv_wlm_service_class_config_vw |
service_class |
int |
Y |
svl_qlog_vw |
elapsed |
int |
Y |
svl_qlog_vw |
query |
int |
Y |
stl_alert_event_log_vw |
query |
int |
Y |
stl_alert_event_log_vw |
event |
varchar |
Y |
stl_alert_event_log_vw |
solution |
varchar |
N |
stl_alert_event_log_vw |
pid |
int |
N |
stl_alert_event_log_vw |
event_time |
timestamp |
N |
svv_table_info_vw |
database |
varchar |
N |
svv_table_info_vw |
table |
varchar |
Y |
svv_table_info_vw |
size |
int |
N |
svv_table_info_vw |
pct_used |
numeric |
N |
svv_table_info_vw |
tbl_rows |
numeric |
Y |
stv_sessions_vw |
starttime |
timestamp |
Y |
stv_sessions_vw |
process |
int |
Y |
stv_sessions_vw |
db_name |
varchar |
N |
stv_sessions_vw |
timeout_sec |
int |
N |
stv_sessions_vw |
user_name |
varchar |
Y |
stl_load_errors_vw |
query |
int |
Y |
stl_load_errors_vw |
line_number |
int |
N |
stl_load_errors_vw |
session |
int |
N |
stl_load_errors_vw |
colname |
varchar |
N |
stl_load_errors_vw |
starttime |
timestamp |
N |
stl_load_errors_vw |
tbl |
int |
N |
stl_load_errors_vw |
filename |
varchar |
N |
stl_load_errors_vw |
err_code |
int |
N |
stl_load_errors_vw |
err_reason |
varchar |
Y |
stl_load_errors_vw |
userid |
int |
Y |
stv_node_storage_capacity_vw |
capacity |
int |
Y |
stv_node_storage_capacity_vw |
used |
int |
Y |
stv_node_storage_capacity_vw |
node |
int |
Y |
stl_ddltext_vw |
pid |
int |
Y |
stl_plan_info_vw |
nodeid |
int |
Y |
stl_plan_info_vw |
query |
int |
Y |
svl_query_metrics_summary_vw |
query |
int |
Y |
svl_s3query_summary_vw |
query |
int |
Y |



