Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp
SpotApps are ThoughtSpot’s out-of-the-box solution templates built for specific use cases and data sources. They are built on ThoughtSpot Modeling Language (TML) Blocks, which are pre-built pieces of code that are easy to download and implement directly from the product.
The Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp mimics the Databricks data model. When you deploy it, ThoughtSpot creates several Worksheets, Answers, and Liveboards, based on your Databricks data in your cloud data warehouse.
This is a sample Liveboard, created after you deploy the Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp:
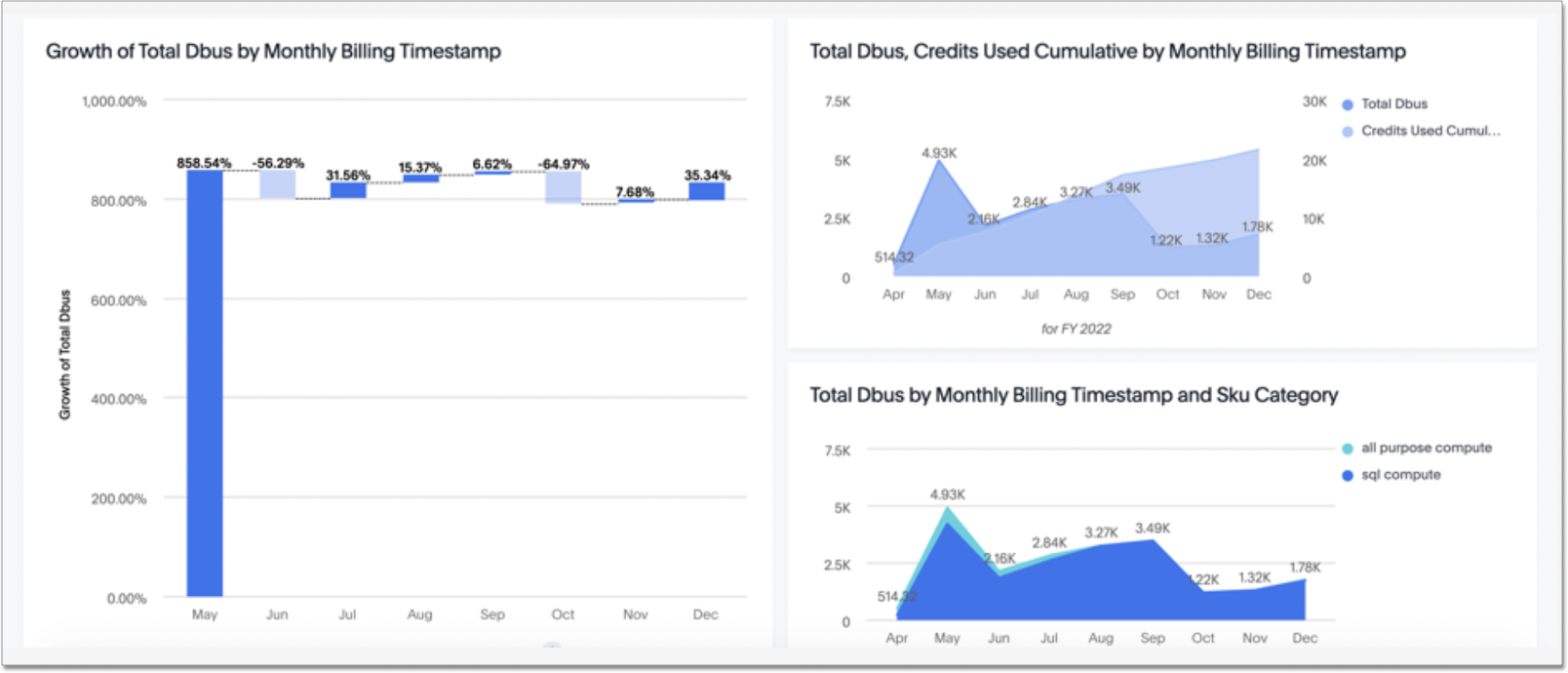
Use the Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp to manage costs and investigate query performance. Track how and where your users consume Databricks Units (DBUs), and investigate latency issues with database queries. You can also review your tables' Z-Ordering.
Prerequisites
Before you can deploy the Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp, you must complete the following prerequisites:
-
Review the required tables and columns for the SpotApp.
-
Ensure that your columns match the required column type listed in the schema for your SpotApp.
-
Obtain credentials and SYSADMIN privileges to connect to Databricks. The cloud data warehouse must contain the data you would like ThoughtSpot to use to create Answers, Liveboards, and Worksheets. Refer to the connection reference for Databricks for information about required credentials.
-
The connection name for each new SpotApp must be unique.
-
Administrator access to Databricks
-
Access to the following Databricks tables in your cloud data warehouse. Refer to Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp schema for more details.
-
ENDPOINTS
-
QUERIES
-
BILLING
-
-
Run the required Python script in your cloud data warehouse. Refer to Run Python script.
Run Python script
Run the following Python script on your Databricks instance. It helps load the Databricks data into tables. Replace any parts of the script that say UPDATE with your specific information, such as the hostid, accountid, and authorization token.
| You must run this Python script on the Databricks cloud data warehouse. |
Python script:
Open the dropdown menu to view the Python script.
import requests
from datetime import date, datetime, timedelta
from dateutil.relativedelta import relativedelta
from pyspark.sql.functions import from_unixtime, lit, json_tuple
#from pyspark.sql.types import StructType, StructField, StringType, IntegerType, DoubleType, ArrayType, DateType
from delta.tables import *
import time
from base64 import b64encode
import io
import pandas as pd
from pandas import json_normalize
import json
# If you want to run this notebook yourself, you need to create a Databricks personal access token,
# https://docs.databricks.com/sql/user/security/personal-access-tokens.html
# store it using our secrets API, and pass it in through the Spark config, such as this:
# spark.pat_token {{secrets/query_history_etl/user}}, or Azure Keyvault.
WORKSPACE_HOST = 'https://UPDATE_ENTERHOSTID.cloud.databricks.com' #https://docs.databricks.com/administration-guide/account-settings/billable-usage-download-api.html
ENDPOINTS_URL = "{0}/api/2.0/sql/endpoints".format(WORKSPACE_HOST) #https://docs.databricks.com/sql/api/sql-endpoints.html
#QUERY API PARAMETERS
MAX_RESULTS_PER_PAGE = 25000
MAX_PAGES_PER_RUN = 500
QUERIES_URL = "{0}/api/2.0/sql/history/queries".format(WORKSPACE_HOST) #https://docs.databricks.com/sql/api/query-history.html
# We will fetch all queries that were started between this number of hours ago, and now()
# Queries that are running for longer than this will not be updated.
# Can be set to a much higher number when backfilling data, for example when this Job didn't
# run for a while.
NUM_HOURS_TO_UPDATE = 24
START_DATE = datetime.now() - timedelta(hours=NUM_HOURS_TO_UPDATE)
#ACCOUNTS API
ACCOUNTS_HOST = 'https://accounts.cloud.databricks.com'
ACCOUNT_ID = 'UPDATE_ACCOUNT_ID' #available from admin portal
START_MONTH = (datetime.today() - relativedelta(months=NUM_MONTHS_TO_UPDATE)).strftime('%Y-%m') # i.e. '2022-01'
END_MONTH = datetime.today().strftime('%Y-%m')
PERSONAL_DATA = True
BILLING_URL = "{0}/api/2.0/accounts/{1}/usage/download?start_month={2}&end_month={3}&personal_data={4}".format(ACCOUNTS_HOST,ACCOUNT_ID,START_MONTH, END_MONTH, PERSONAL_DATA)
#DATABASE_NAME = "query_history_etl"
DATABASE_NAME = "spotapps"
ENDPOINTS_TABLE_NAME = "endpoints"
QUERIES_TABLE_NAME = "queries"
BILLING_TABLE_NAME = "billing"
#Databricks secrets API
#https://docs.databricks.com/dev-tools/api/latest/authentication.html
#auth_header = {"Authorization" : "Bearer " + spark.conf.get("spark.pat_token")}
#Azure KeyVault
#auth_header = {"Authorization" : "Bearer " + dbutils.secrets.get(scope = "<scope-name>", key = "<key-name>")}
#hardcoded authorisation token
auth_header = {"Authorization" : "Bearer UPDATE_AUTHORISATION_TOKEN"}
#basic auth required for billing API
auth_header_basic = {
"Authorization": "Basic {}".format(
b64encode(bytes("UPDATE_USER_EMAIL:UPDATE_USER_PWD", "utf-8")).decode("ascii")
)
}
def check_table_exist(db_tbl_name):
table_exist = False
try:
spark.read.table(db_tbl_name) # Check if spark can read the table
table_exist = True
except:
pass
return table_exist
def current_time_in_millis():
return round(time.time() * 1000)
def get_boolean_keys(arrays):
# A quirk in Python's and Spark's handling of JSON booleans requires us to converting True and False to true and false
boolean_keys_to_convert = []
for array in arrays:
for key in array.keys():
if type(array[key]) is bool:
boolean_keys_to_convert.append(key)
#print(boolean_keys_to_convert)
return boolean_keys_to_convert
notebook_start_execution_time = current_time_in_millis()
spark.sql("CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS {}".format(DATABASE_NAME))
response = requests.get(ENDPOINTS_URL, headers=auth_header)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(response.text)
response_json = response.json()
endpoints_json = response_json["endpoints"]
# A quirk in Python's and Spark's handling of JSON booleans requires us to converting True and False to true and false
boolean_keys_to_convert = set(get_boolean_keys(endpoints_json))
for endpoint_json in endpoints_json:
for key in boolean_keys_to_convert:
endpoint_json[key] = str(endpoint_json[key]).lower()
endpoints = spark.read.json(sc.parallelize(endpoints_json))
display(endpoints)
endpoints.write.format("delta").option("overwriteSchema", "true").mode("overwrite").saveAsTable(DATABASE_NAME + "." + ENDPOINTS_TABLE_NAME)
START_DATE = datetime.now() - timedelta(hours=NUM_HOURS_TO_UPDATE)
start_time_ms = START_DATE.timestamp() * 1000
end_time_ms = datetime.now().timestamp() * 1000
next_page_token = None
has_next_page = True
pages_fetched = 0
while (has_next_page and pages_fetched < MAX_PAGES_PER_RUN):
print("Starting to fetch page " + str(pages_fetched))
pages_fetched += 1
if next_page_token:
# Can not set filters after the first page
request_parameters = {
"max_results": MAX_RESULTS_PER_PAGE,
"page_token": next_page_token,
"include_metrics": True
}
else:
request_parameters = {
"max_results": MAX_RESULTS_PER_PAGE,
"filter_by": {"query_start_time_range": {"start_time_ms": start_time_ms, "end_time_ms": end_time_ms}},
"include_metrics": True
}
print ("Request parameters: " + str(request_parameters))
response = requests.get(QUERIES_URL, headers=auth_header, json=request_parameters)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(response.text)
response_json = response.json()
next_page_token = response_json["next_page_token"]
has_next_page = response_json["has_next_page"]
boolean_keys_to_convert = set(get_boolean_keys(response_json["res"]))
for array_to_process in response_json["res"]:
for key in boolean_keys_to_convert:
array_to_process[key] = str(array_to_process[key]).lower()
#unable to flatten metrics json with spark
#query_results = spark.read.json(sc.parallelize(response_json["res"]))
#normalise the json into a pandas datafram
query_results_df = json_normalize(response_json["res"])
#convert pandas df to spark
query_results = spark.createDataFrame(query_results_df)
# create date time fields from unixtime(ms)
query_results_clean = query_results \
.withColumn("query_start_time", from_unixtime(query_results.query_start_time_ms / 1000, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss').cast("timestamp")) \
.withColumn("query_end_time", from_unixtime(query_results.query_end_time_ms / 1000, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss').cast("timestamp"))
# The error_message column is not present in the REST API response when none of the queries failed.
# In that case we add it as an empty column, since otherwise the Delta merge would fail in schema
# validation
if "error_message" not in query_results_clean.columns:
query_results_clean = query_results_clean.withColumn("error_message", lit(""))
# was getting ad hoc error on merge with _corrupt_record, added to dataset as empty string
if "_corrupt_record" not in query_results_clean.columns:
query_results_clean = query_results_clean.withColumn("_corrupt_record", lit(""))
if not check_table_exist(db_tbl_name="{0}.{1}".format(DATABASE_NAME, QUERIES_TABLE_NAME)):
# TODO: Probably makes sense to partition and/or Z-ORDER this table.
query_results_clean.write.format("delta").saveAsTable("{0}.{1}".format(DATABASE_NAME, QUERIES_TABLE_NAME))
else:
# Merge this page of results into the Delta table. Existing records that match on query_id have
# all their fields updated (needed because the status, end time, and error may change), and new
# records are inserted.
queries_table = DeltaTable.forName(spark, "{0}.{1}".format(DATABASE_NAME, QUERIES_TABLE_NAME))
queries_table.alias("queryResults").merge(
query_results_clean.alias("newQueryResults"),
"queryResults.query_id = newQueryResults.query_id") \
.whenMatchedUpdateAll() \
.whenNotMatchedInsertAll() \
.execute()
response = requests.get(BILLING_URL, headers=auth_header_basic)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(response.text)
billing_results = spark.createDataFrame(pd.read_csv(io.StringIO(response.content.decode('utf-8'))))
billing_results = billing_results.withColumn("timestamp", billing_results["timestamp"].cast("timestamp"))
#print (billing_results)
if not check_table_exist(db_tbl_name="{0}.{1}".format(DATABASE_NAME, BILLING_TABLE_NAME)):
# TODO: Probably makes sense to partition and/or Z-ORDER this table.
billing_results.write.format("delta").saveAsTable("{0}.{1}".format(DATABASE_NAME, BILLING_TABLE_NAME))
else:
#Overwright table TODO MERGE LOGIC
spark.sql("DROP TABLE {0}.{1}".format(DATABASE_NAME, BILLING_TABLE_NAME))
billing_results.write.format("delta").saveAsTable("{0}.{1}".format(DATABASE_NAME, BILLING_TABLE_NAME))
print("Time to execute: {}s".format((current_time_in_millis() - notebook_start_execution_time) / 1000))Deploy the Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp
After you complete the prerequisites, you are ready to deploy the Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp and begin leveraging its pre-built content.
To deploy the Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp, refer to Deploying SpotApps.
Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp schema
The following table describes the schema for the Databricks Storage and Performance SpotApp.
| Table | Column | Column type | Required column |
|---|---|---|---|
ENDPOINTS |
NAME |
VARCHAR |
Y |
ENDPOINTS |
ID |
VARCHAR |
Y |
QUERIES |
ENDPOINT_ID |
VARCHAR |
Y |
QUERIES |
QUERY_TEXT |
VARCHAR |
Y |
QUERIES |
STATUS |
VARCHAR |
N |
QUERIES |
USER_NAME |
VARCHAR |
N |
QUERIES |
QUERY_START_TIME |
DATE_TIME |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.READ_CACHE_BYTES |
INTEGER |
N |
QUERIES |
METRICS.READ_PARTITIONS_COUNT |
INTEGER |
N |
QUERIES |
METRICS.READ_REMOTE_BYTES |
INTEGER |
N |
QUERIES |
METRICS.SPILL_TO_DISK_BYTES |
INTEGER |
N |
QUERIES |
METRICS.ROWS_READ_COUNT |
INTEGER |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.READ_FILES_COUNT |
INTEGER |
N |
QUERIES |
METRICS.ROWS_PRODUCED_COUNT |
INTEGER |
N |
QUERIES |
METRICS.RESULT_FROM_CACHE |
BOOLEAN |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.WRITE_REMOTE_BYTES |
INTEGER |
N |
QUERIES |
ERROR_MESSAGE |
VARCHAR |
Y |
QUERIES |
QUERY_ID |
VARCHAR |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.TOTAL_TIME_MS |
INTEGER |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.EXECUTION_TIME_MS |
DOUBLE |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.COMPILATION_TIME_MS |
DOUBLE |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.TASK_TOTAL_TIME_MS |
INTEGER |
Y |
QUERIES |
METRICS.RESULT_FETCH_TIME_MS |
INTEGER |
Y |
BILLING |
DBUS |
DOUBLE |
Y |
BILLING |
MACHINEHOURS |
DOUBLE |
Y |
BILLING |
CLUSTERNODETYPE |
VARCHAR |
Y |
BILLING |
CLUSTERNAME |
VARCHAR |
Y |
BILLING |
CLUSTERID |
VARCHAR |
Y |
BILLING |
WORKSPACEID |
INTEGER |
N |
BILLING |
CLUSTEROWNERUSERID |
INTEGER |
N |
BILLING |
SKU |
VARCHAR |
Y |
BILLING |
TIMESTAMP |
DATE_TIME |
Y |



