Managing authentication with SAML
ThoughtSpot integrates with SAML for authentication.
|
This article contains instructions for managing SAML authentication if your company does NOT use IAMv2. IAMv2 is off by default. If the SAML section of the Admin Console is called Authentication: SAML, your company is not using IAMv2. If the SAML section of the Admin Console is called SAML integration, your company is using IAMv2. Refer to Managing authentication with SAML using IAMv2. |
|
If your organization uses multi-tenancy with Orgs, you must be a cluster administrator to manage SAML authentication, not an Org administrator. You manage SAML authentication for the whole cluster. You cannot set it separately for each Org. To ensure SAML authentication works smoothly in an Orgs environment, you must include Orgs mapping in your IDP assertion. See IDP metadata XML file. If you map Orgs with SAML, you can’t also map groups. If you are using Multi-tenancy with Orgs, we do not currently support using IAMv2. |
SAML SSO authentication
ThoughtSpot supports the Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication method with the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) authentication and authorization framework. With SAML SSO, users can authenticate to the SAML identity provider (IDP) at your federation to access the ThoughtSpot application, or the embedded ThoughtSpot content in an external web application. It also allows them to navigate seamlessly between different application interfaces with their existing credentials.
By default, local authentication is enabled. After you configure SAML authentication, you can configure the ThoughtSpot login page to default to SSO login by contacting ThoughtSpot Support. Note that if you change the default login experience to SSO, local users cannot authenticate.
Use this article to learn how to configure a SAML integration with an external IDP. To configure SAML in an embedded environment, refer to SAML SSO authentication.
SAML authentication with multiple IDPs
You may have multiple groups of users who need to sign in to ThoughtSpot but are managed by separate IDPs. You can configure SAML SSO login for more than one Identity Provider. However, when a user logs in to ThoughtSpot from the ThoughtSpot login page, they can only sign in from the default IDP you configured with ThoughtSpot Support. To use the other, non-default IDPs, users must sign in from the other IDPs' login pages.
To configure SAML authentication with multiple IDPs, contact ThoughtSpot Support.
| ThoughtSpot supports configuration of a maximum of 5 IDPs. |
About SAML authentication
The SAML SSO authentication involves several entities and components.
SAML entities
SAML is an XML standard that allows secure exchange of user authentication and authorization data between trusted partners. It enables the following entities to exchange identity, authentication, and authorization information:
-
Identity Provider (IDP)
The Identity Management system that maintains the user identity information. IDP acts as a SAML authority and authenticates SSO users. ThoughtSpot supports SAML authentication framework with popular Identity Providers such as Okta, Azure Active Directory, PingFederate, Microsoft AD FS, and Onelogin. This is not an exhaustive list. To determine if ThoughtSpot supports your preferred IDP, talk to your ThoughtSpot contact.
After you complete the SAML configuration in ThoughtSpot that this article describes, refer to your Identity Provider’s SAML documentation for specific information on setting up SAML with that IDP.
-
Service Provider (SP)
The provider of a business function or application service; for example ThoughtSpot. The SP relies on the IDP to authenticate users before allowing access to its services.
-
Federated user
A user whose identity information is managed by the IDP. The federated users have SSO credentials and authenticate to IDP to access various application services.
SAML assertion and attributes
Both SP-initiated and IDP-initiated authentication workflows rely upon assertions that are exchanged between the SAML endpoints through a web browser.
Some of the most commonly used elements are:
-
SAML assertion
The user authentication and authorization information issued by the IDP. SAML assertions contain all the information necessary for a service provider to confirm if the user identity is valid.
ThoughtSpot supports 2 methods to increase the duration of validity for your SAML assertion: the
SessionNotOnOrAfterattribute and themaxAuthenticationAgeparameter. You can ask ThoughtSpot to disable either one of these checks. If you use both, and either check fails, ThoughtSpot does not authenticate the user. Some IDPs do not support use ofSessionNotOnOrAfter. If your IDP does not support use ofSessionNotOnOrAfter, remove that attribute from your IDP assertion and ask ThoughtSpot Support to enablemaxAuthenticationAge. -
Metadata
Data in the XML format to establish interoperability between the IDP and SP. It contains the URLs of the endpoints, entity ID, and so on.
-
Assertion Services Consumer (ACS) URL
The endpoint URL to which the user’s browser sends the SAML response received from the IDP after authenticating a user.
-
Entity ID
A unique service name to identify the client application from which the SSO login request originates.
-
SAML attributes
The attributes associated with the user; for example, the username and email address. In a multi-tenancy with Orgs environment, you must include an Orgs attribute that contains all the Orgs the user belongs to.
Enable SAML authentication
You need admin privileges to enable SAML SSO authentication.
-
If you are using Multi-tenancy with Orgs, ask ThoughtSpot Support to enable SAML integration in your environment. After ThoughtSpot Support enables SAML integration, you can configure SAML for your environment.
-
Configure the ThoughtSpot application instance on your IDP server.
-
If you are using Identity and Access Management V2, you must whitelist the following URL in your IDP:
https://identity.thoughtspotlogin.cloud/.
-
-
Sign in to your ThoughtSpot application instance.
-
From the top navigation bar, select the Admin tab.
-
Select SAML from the side navigation bar that appears.
If your organization uses multi-tenancy with Orgs, ensure that you are in the Primary Org, in the All orgs section of the Admin Console. You manage SAML authentication for the whole cluster. You cannot set it separately for each Org.
-
Select the Configure button in the middle of the screen.
-
Fill in the following parameters:
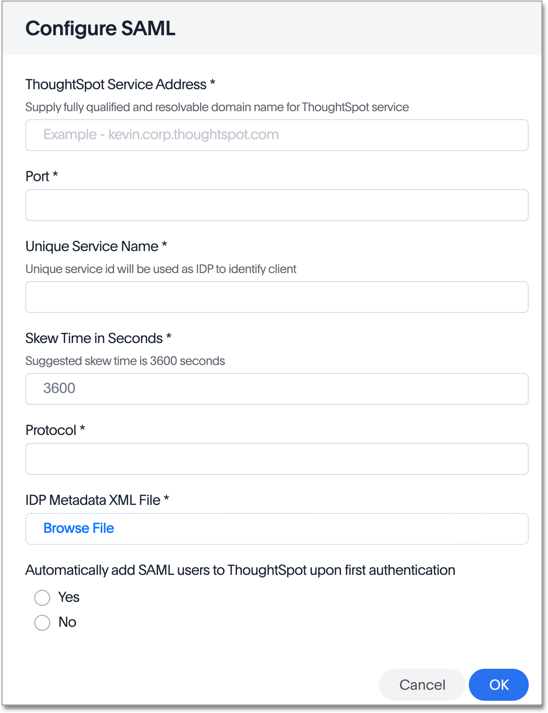
- ThoughtSpot Service Address
-
A fully qualified and resolvable domain name for the ThoughtSpot service.
This must be in the format <cluster-name>.thoughtspot.cloud.
- Port
-
Enter
443in this box.This is the port of the server where your ThoughtSpot instance is running.
- Unique Service Name
-
The unique key used by your Identity Provider to identify the client.
For example, urn:thoughtspot:callosum:saml, or https://ssoappname.microsoft.com/ab12c3de4.
This is also called the SP Entity ID.
- Skew Time in Seconds
-
The allowed skew time, after which the authentication response is rejected and sent back from the IDP. 86400 is a popular choice.
The default is 3600.
- Protocol
-
The connection protocol for ThoughtSpot.
Use
https.
- IDP Metadata XML File
-
The absolute path to your Identity Provider’s metadata file. This file is provided by your IDP. You need this file so that the configuration persists over upgrades. It is a best practice to set it up on persistent/HA storage (NAS volumes) or in the same absolute path on all nodes in the cluster. For example, idp-meta.xml. If your IDP needs an Assertion Consumer Service URL to create the metadata file, use
https://<hostname_or_IP>:443/callosum/v1/saml/SSO. Note that this URL is case-sensitive.If your IDP does not allow you to import the IDP metadata XML file, you must map values between ThoughtSpot and your IDP manually. This allows the ThoughtSpot system to automatically pick up certain attributes and subjects, such as a user’s email address, display name, and username. In a multi-tenancy with Orgs environment, you must include an Orgs attribute that contains all the Orgs to which the user belongs. Map the username attribute value in your IDP (
userPrincipalNamein Okta, for example) toNameId, map the email attribute value tomail, and map the display name subject value todisplayName. Attributes and subjects appear in separate sections of your SAML assertion. It is mandatory to fill out the mail field. If your company cannot meet this requirement, contact ThoughtSpot Support.If your company uses Orgs, it is also mandatory to include mapping for the Orgs attribute. If you do not including Orgs mapping, all users get assigned only to the Primary Org. In the Org mapping, you must include all the Orgs to which the user belongs. Here is a sample Orgs attribute:
<saml2:Attribute Name="orgs NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified"> <saml2:AttributeValue xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">Primary </saml2:AttributeValue> <saml2:AttributeValue xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">testorg </saml2:AttributeValue> </saml2:Attribute>For additional support with the attribute statements, refer to your IDP’s SAML documentation. ThoughtSpot supports SAML authentication framework with popular Identity Providers such as Okta, Azure Active Directory, PingFederate, Microsoft AD FS, and Onelogin. This is not an exhaustive list. To determine if ThoughtSpot supports your preferred IDP, talk to your ThoughtSpot contact.
- Automatically add SAML users to ThoughtSpot upon first authentication
-
Choose whether to add SAML users to ThoughtSpot when they first authenticate. If you choose 'yes', then new users will be automatically created in ThoughtSpot upon first successful SSO login. If you choose 'no', then SAML users will not be added in ThoughtSpot upon first successful SSO login. Instead, you must add users manually.
-
After you fill in all parameters, select OK.
-
When the configuration is complete, download ThoughtSpot’s metadata file,
spring_saml_metadata.xml. This file contains the public key you need if you want to encrypt your SAML assertions. To download this file, navigate tohttps://<hostname-or-IP>/callosum/v1/saml/metadata/. The file automatically downloads.
Configure the IDP
To enable the IDP to recognize your host application and ThoughtSpot as a valid service provider, you must configure the IDP with required attributes and metadata.
ThoughtSpot supports SAML authentication with several identity and access management providers, such as Okta, Azure Active Directory, PingFederate, Microsoft AD FS, Onelogin and so on. If you want to use one of these providers as your IDP, make sure you read the SAML configuration steps described in the Identity provider’s documentation site.
To determine if ThoughtSpot supports your preferred IDP, contact ThoughtSpot Support.
Complete your configuration of the IDP using the IDP’s SAML documentation.
Upload or copy the contents of the spring_saml_metadata.xml to your IDP server.
This file contains the public key you need if you want to encrypt your SAML assertions.
If you did not download the spring_saml_metadata.xml file, navigate to https://<your_ThoughtSpot_hostname-or-IP>/callosum/v1/saml/metadata/.
The file automatically downloads.
When configuring SAML 2.0, make sure you map the SAML user attributes and subjects to appropriate fields.
This allows the ThoughtSpot system to automatically pick up certain attributes and subjects, such as a user’s email address, display name, and username.
Map the username attribute value in your IDP (userPrincipalName in Okta, for example) to NameId, map the email attribute value to mail, and map the display name subject value to displayName.
It is mandatory to fill out the mail field.
If your company cannot meet this requirement, contact ThoughtSpot Support.
If your IDP does not allow you to import the IDP metadata XML file, you must map these values manually.
If your company uses Orgs, it is also mandatory to include mapping for the Orgs attribute. You must include all the Orgs to which the user belongs. Here is a sample Orgs attribute:
<saml2:Attribute
Name="orgs
NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified">
<saml2:AttributeValue
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:type="xs:string">Primary
</saml2:AttributeValue>
<saml2:AttributeValue
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:type="xs:string">testorg
</saml2:AttributeValue>
</saml2:Attribute>| You can map Orgs and groups with SAML. |
SAML group and Org mapping
You can map your SAML groups and Orgs from your IDP to your ThoughtSpot. For more information about Orgs, see Orgs. SAML group and Org mapping means that you do not have to manually recreate your groups and Orgs in ThoughtSpot, if they are already present in your IDP. Refer to Configure SAML group mapping.
Use SSO login by default
After you configure SAML authentication, a new option appears on the login page that allows users to sign in using SSO, while still allowing local users to sign in.
To only allow SSO login by default, contact ThoughtSpot Support. Note that if you change the default login experience to SSO, local users cannot authenticate.
Related information



