Configure Azure AD OAuth for a Starburst connection
With Azure AD OAuth, the authorization server generates an access token from Azure AD on behalf of the ThoughtSpot user which authenticates them with Starburst and authorizes ThoughtSpot to query the database using their Starburst user account.
| The steps provided here are an example of how you can configure Azure AD OAuth for external OAuth. You can use any OAuth flow provided that you can get the information required for the security integration. The following steps provide a guide for getting the information required to create the security integration for Starburst. |
| Be sure to consult your organization’s security policies for configuring an authorization server to make sure you meet all requirements. |
Creating an external OAuth token using Azure AD on behalf of the user
Part 1: Creating a Starburst OAuth resource
To create a Starburst OAuth resource, do the following:
-
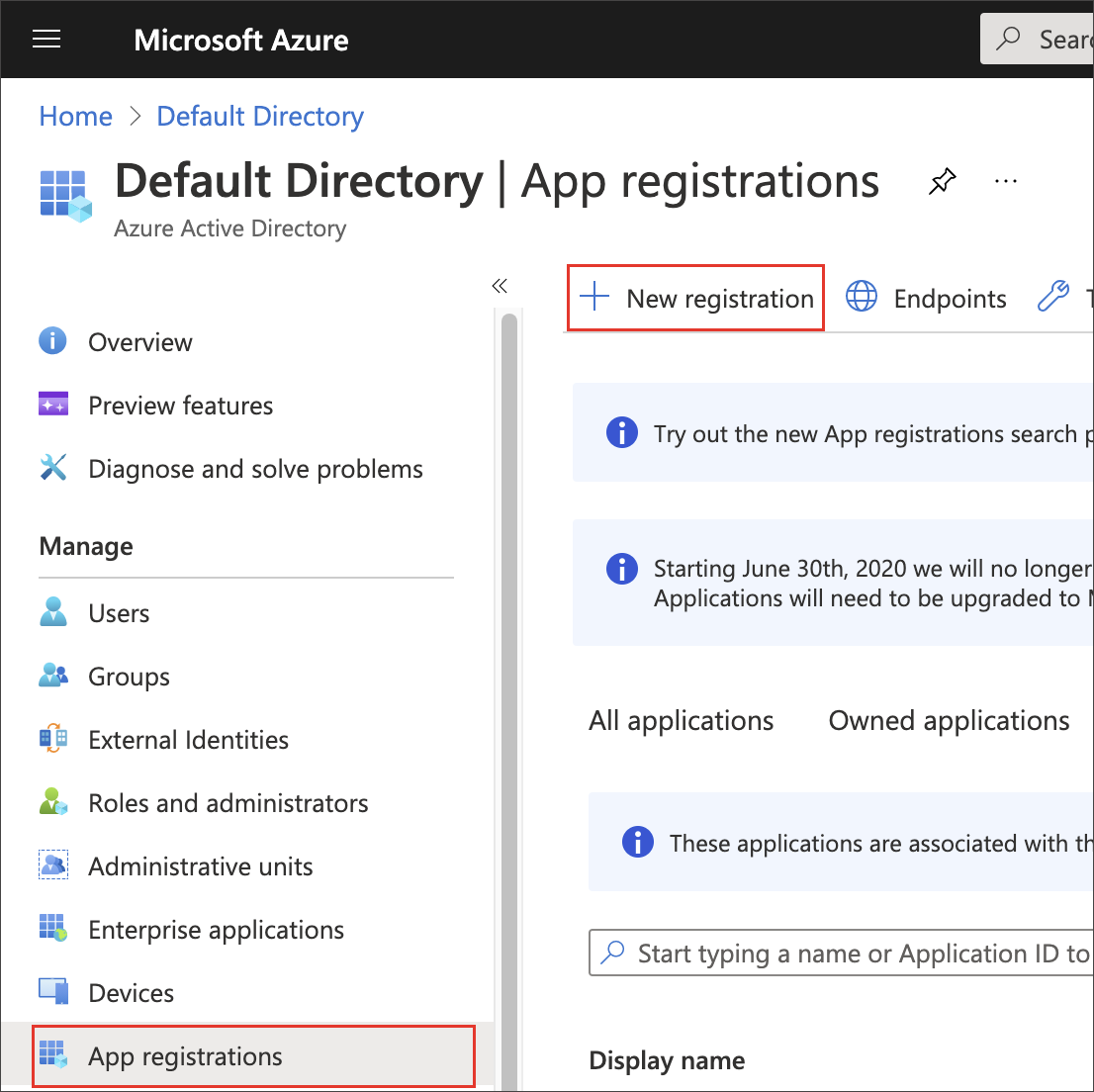
Sign in to the Microsoft Azure Portal.
-
Navigate to Azure Active Directory.

-
Select App registrations, then New registration.
-
For Name, enter a name for your application.
Example:
Starburst Oauth User Resource -
Make sure Supported account types is set to Single Tenant.
-
Select Register.

-
After the application is created, select Expose an API.

-
Next to Application ID URI, select Set and change its value from api://<alphanumeric value> to https://<alphanumeric value> and click Save.

If the Application ID URI is not used, you must create a security integration with audiences using the Starburst Account URL (i.e. <account_identifier>.starburst.com).The Application ID URI must be unique within your organization’s directory, such as https://your.company.com/4d2a8c2b-a5f4-4b86-93ca-ack45667. -
Select Add a scope.
-
For Scope name, enter the name of the Starburst role (example:
session:role-any). -
Select who can consent.
-
Enter an Admin consent display name (example:
Any). -
Enter an Admin consent description.
-
Select Add Scope.
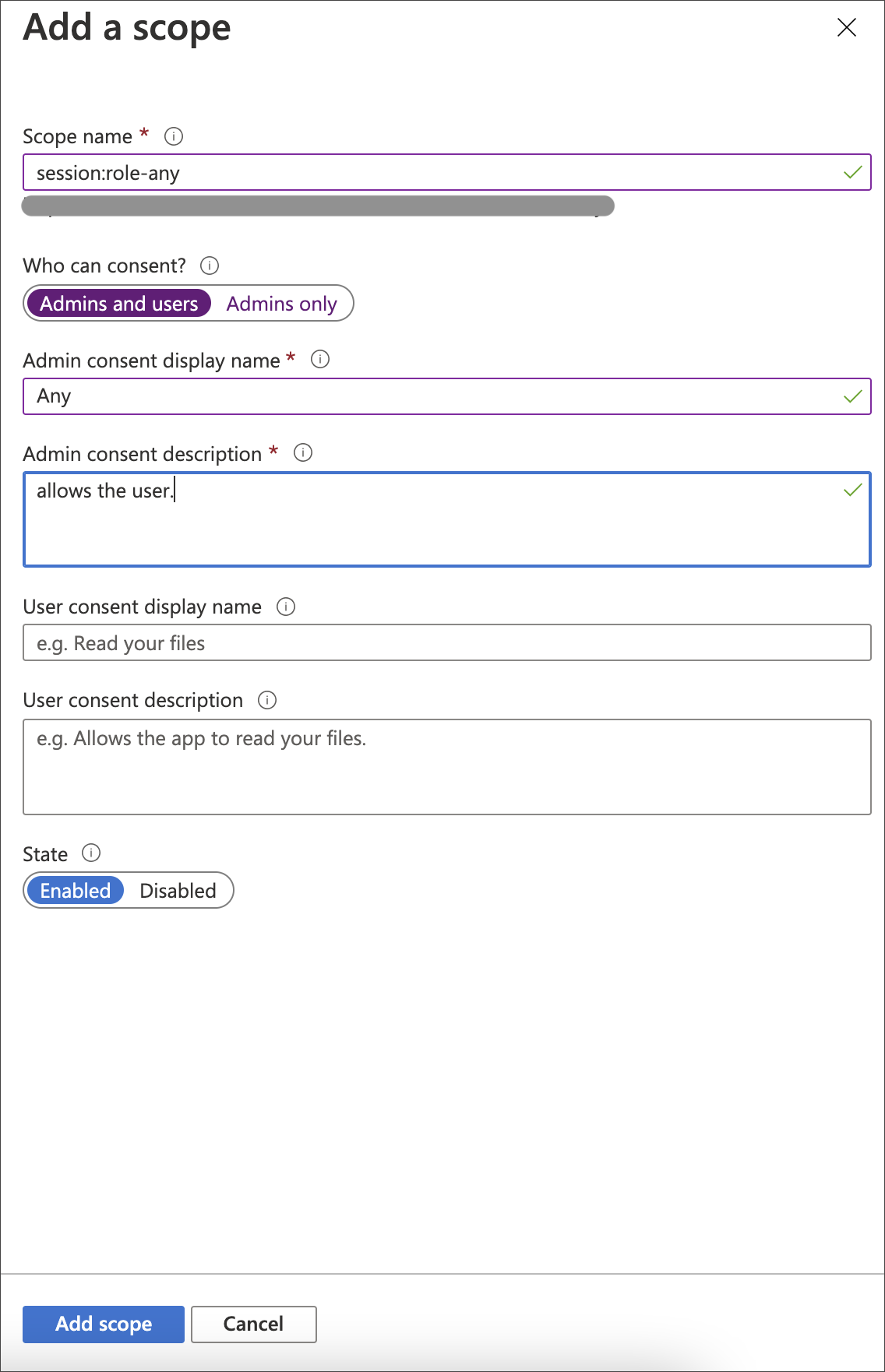
| When you create the scope in your Azure AD application, you must set it to “any” so that a user can later switch to any of their allowed roles when making a JDBC connection using the obtained token. |
Part 2: Creating a Starburst OAuth client app
To create a Starburst OAuth client app, do the following:
-
Sign in to the Microsoft Azure Portal, and navigate to Azure Active Directory, if needed.
-
Select App registrations, and then click New registration.
-
For Name, enter a name for the client (example:
Starburst OAuth Client). -
For Supported account types, make sure it is set to Single tenant.
-
Select Register.
-
Once the app is created, select Overview.
-
From the Application (client) ID field, copy the ID. This ID is referred to as the
<OAUTH_CLIENT_ID>in the steps that follow.
-
Select Authentication, and under Web, specify the redirect URI using the following format:
<https://<public> url of your ThoughtSpot Instance>/callosum/v1/connection/generateTokens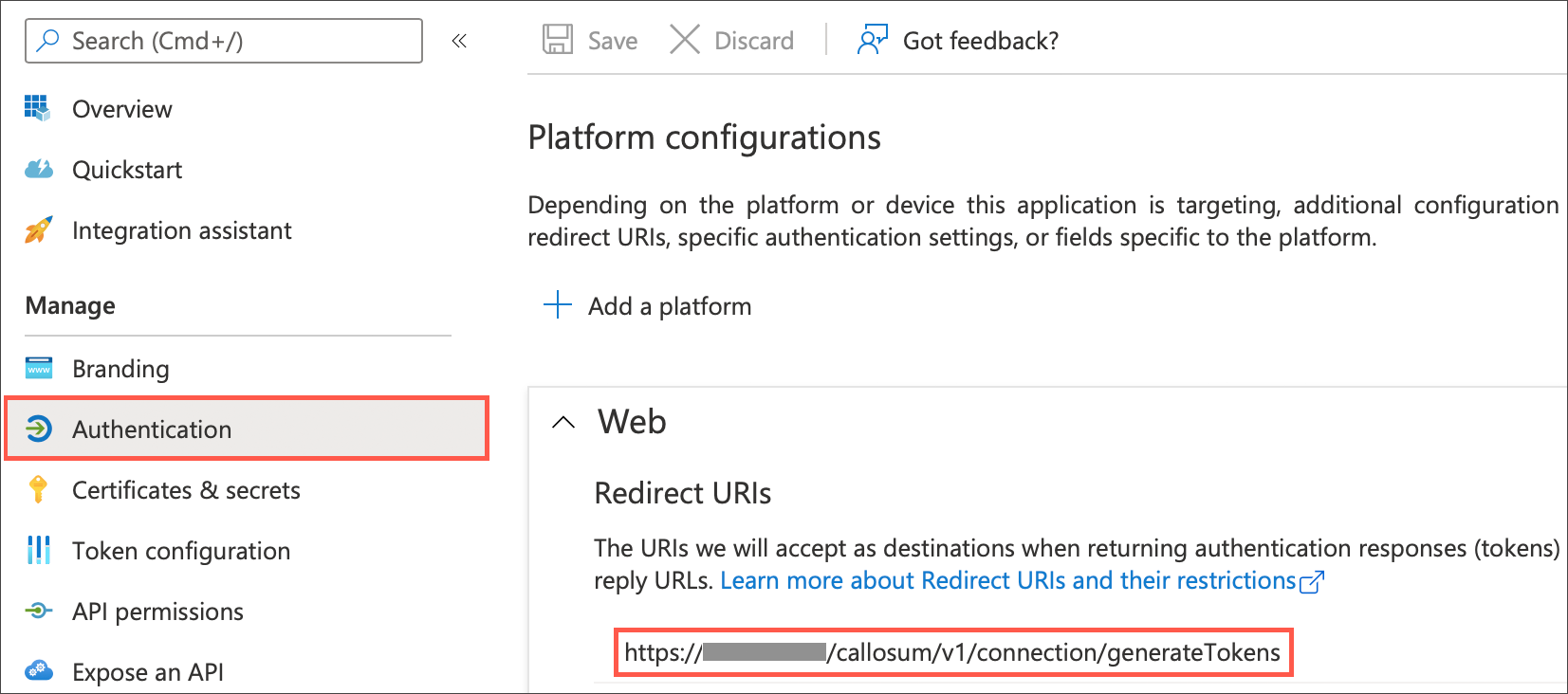
-
Select Certificates & secrets and then New client secret.

-
Copy the Value of the secret you just created. This is referred to as
<OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET>in the steps that follow.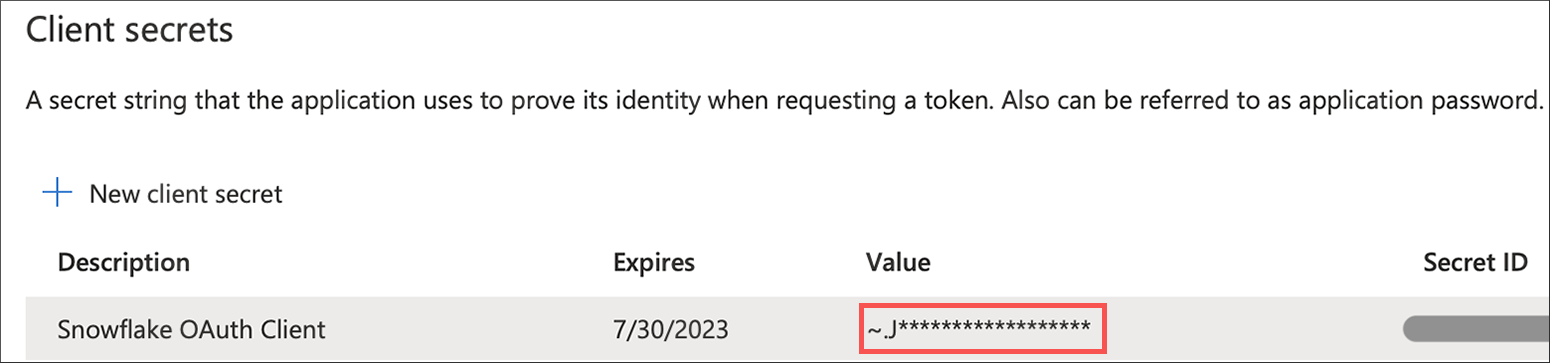
-
Select API permissions, then click Add a permission.

-
Select My APIs.
-
Select the name of the Starburst OAuth Resource you created in Part 1.
-
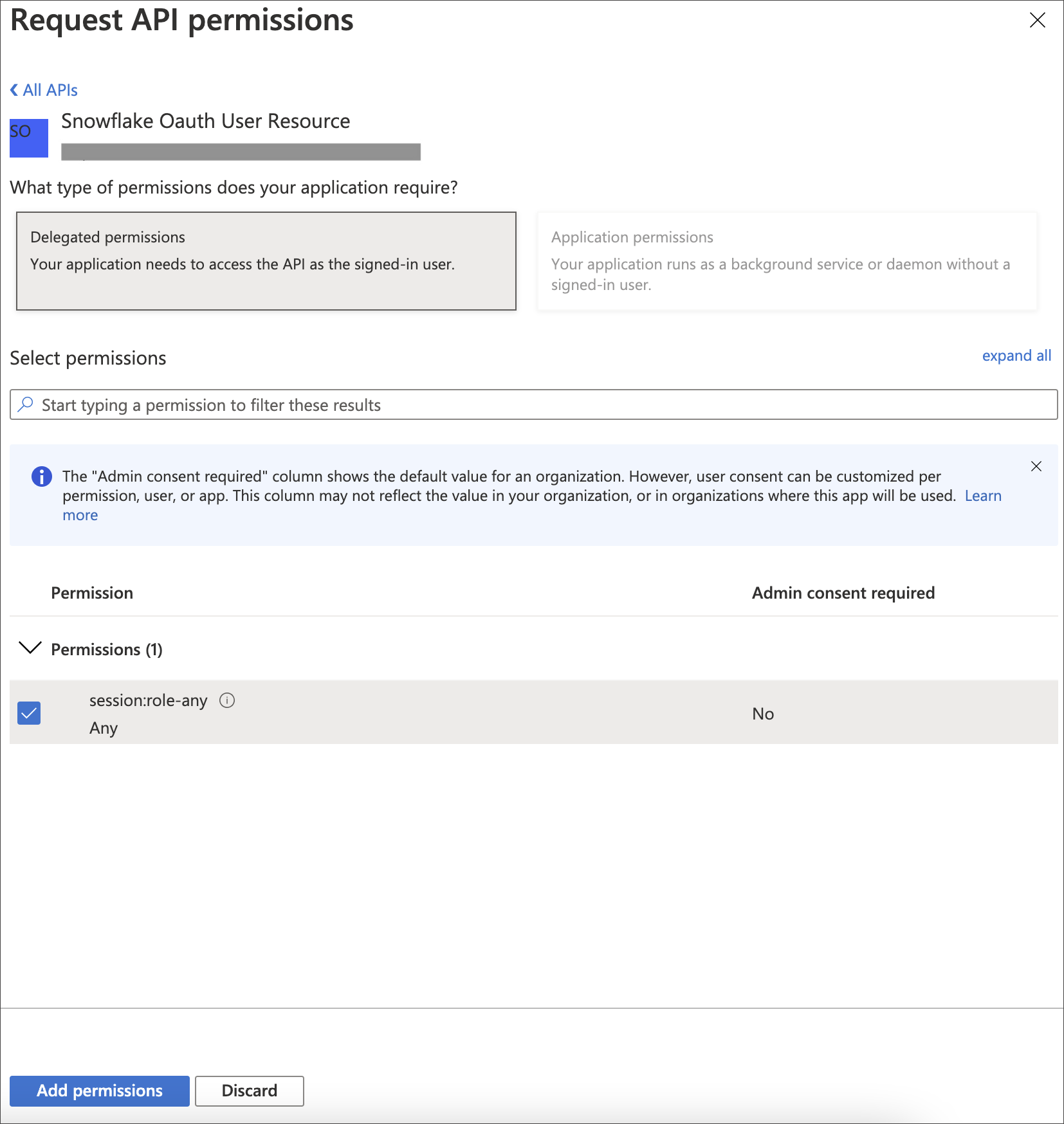
On the Request API permissions page, click the Delegated permissions box, and select the permission related to scope you defined in the application you want to grant to this client.
-
Select Add permissions.
-
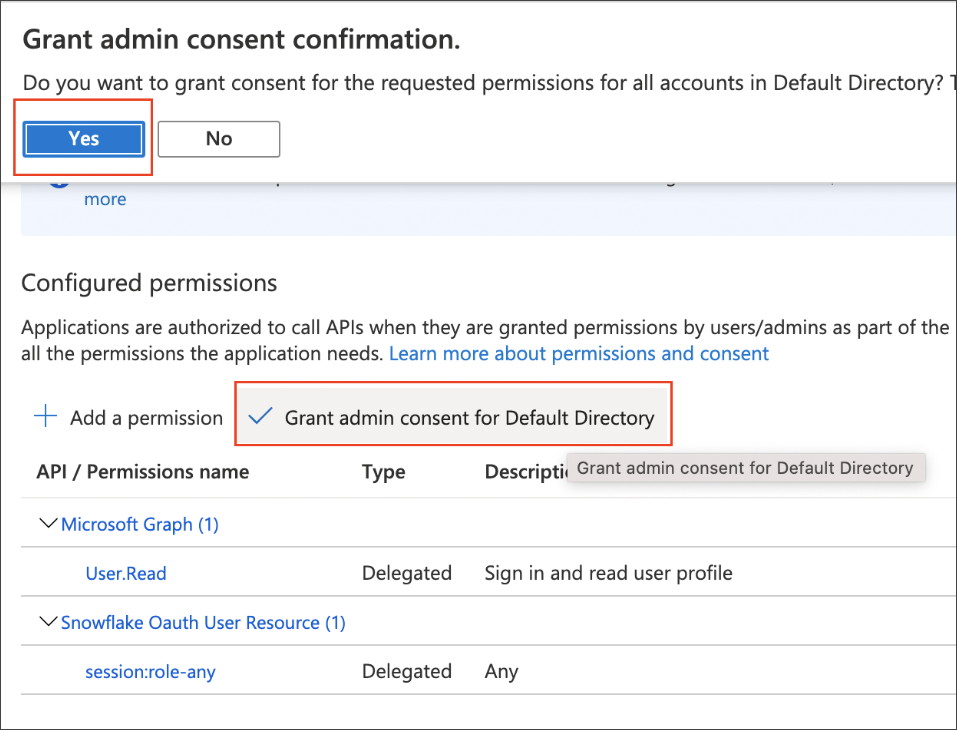
Under Configured permissions, select Grant admin consent for Default Directory, and then click Yes in the confirmation message.
Part 3: Collecting Azure AD information for Starburst
To collect Azure AD information for Starburst, do the following:
-
Sign in to the Microsoft Azure Portal, and navigate to Azure Active Directory, if needed.
-
Go back to the Starburst OAuth Resource App (Starburst Oauth User Resource) to collect the following information:
-
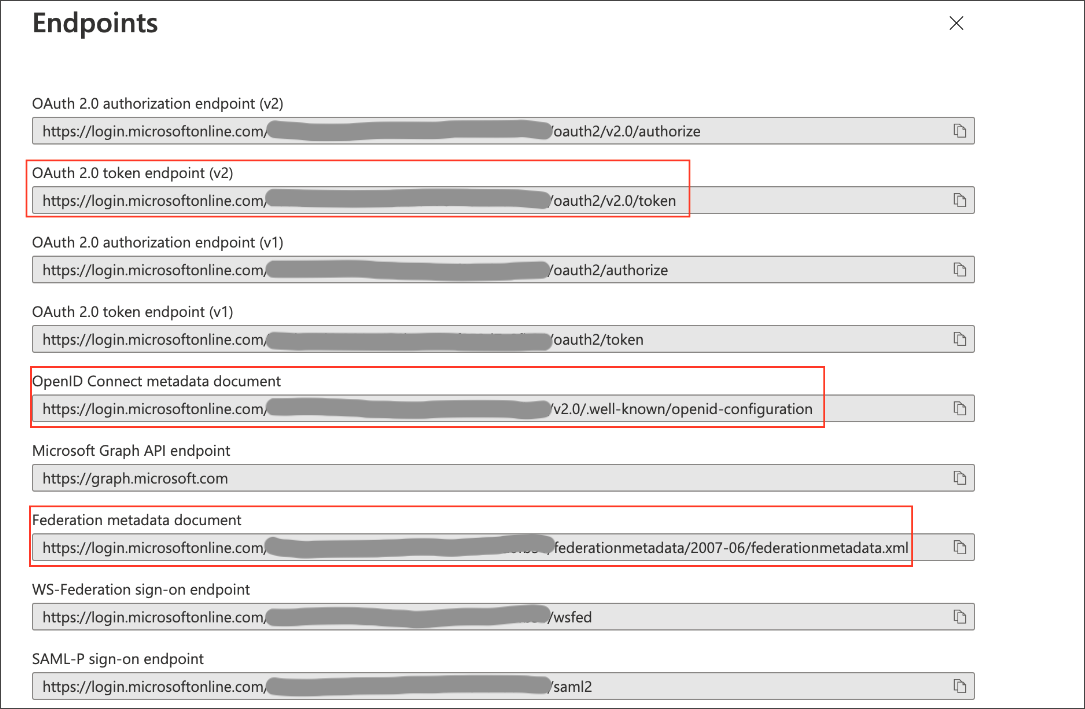
Select Endpoints in the Overview interface.
-
On the right side, copy the OAuth 2.0 token endpoint (v2) and note the URLs for OpenID Connect metadata and Federation Connect metadata.
-
The OAuth 2.0 token endpoint (v2) is referred to as the
<AZURE_AD_OAUTH_TOKEN_ENDPOINT>in the following configuration steps. The endpoint should be similar tohttps://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant_id>/oauth2/v2.0/token/. -
For the OpenID Connect metadata, open in a new browser window.
-
Locate the "jwks_uri" parameter and copy its value.
-
This parameter value will be known as the
<AZURE_AD_JWS_KEY_ENDPOINT>in the following configuration steps. The endpoint should be similar tohttps://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant_id>/discovery/v2.0/keys.
-
-
-
-
For the Federation metadata document, open the URL in a new browser window.
-
Locate the
"entityID"parameter in theXML Root Elementand copy its value. -
This parameter value will be known as the
<AZURE_AD_ISSUER>in the following configuration steps. The entityID value should be similar tohttps://sts.windows.net/<tenant_id>/.
-
-
The OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint (v2) should be similar to
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant_id>/oauth2/v2.0/authorize.
Part 4: Creating an OAuth authorization server in Starburst
In this part you must do the following:
-
Create a security integration in Starburst to ensure that Starburst can securely communicate with Microsoft Azure AD.
-
Validate the tokens from Azure AD.
-
Provide the appropriate Starburst data access to users based on the user role associated with the OAuth token.
If you use SESSION:ROLE-ANY in scope, you must configure the following flag in the security integration: external_oauth_any_role_mode = ‘ENABLE’. This is shown in the optional line of the security integration format example.
|
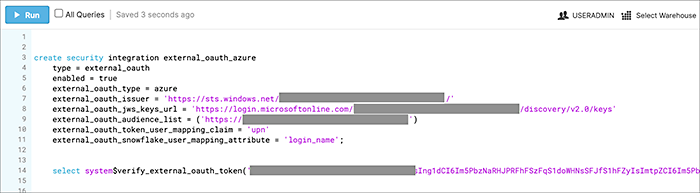
Security integration format
create security integration external_oauth_azure_2
type = external_oauth
enabled = true
external_oauth_type = azure
external_oauth_issuer = '<AZURE_AD_ISSUER>'
external_oauth_jws_keys_url = '<AZURE_AD_JWS_KEY_ENDPOINT>'
external_oauth_audience_list = ('<STARBURST_APPLICATION_ID_URI>')
external_oauth_token_user_mapping_claim = 'upn'
external_oauth_any_role_mode = 'ENABLE' (optional)
external_oauth_starburst_user_mapping_attribute = 'login_name';Example:
When you create the Starburst OAuth Resource Application in Azure AD, if you enter an Application ID URI that is not the Starburst Account URL (i.e.
<account_identifier>.starburst.com), you must add the external_oauth_audience_list parameter to the command with the value <STARBURST_APPLICATION_ID_URI>.
|
Starburst commands
Create user as Azure AD user
CREATE USER testuser PASSWORD = '' LOGIN_NAME = '[email protected]' DISPLAY_NAME = 'AD_TEST_USER';
(Optional) Validating your Azure configuration
To ensure your Azure configuration is correct for use with ThoughtSpot, you can generate an access token.
| This following example is for Azure. The process for other providers is similar. |
You can use either of the following methods to generate your access token:
-
Postman
-
cURL
Method 1: Postman
To validate your configuration using Postman, do the following:
-
Sign in to Postman.
-
Go to the Authorization tab.
-
For Token Name, enter a token name.
-
For Grant Type, select Authorization Code from the menu.
-
For Callback URL, select Authorize using browser.
This should be defined in your OAuth User app(Ex: Starburst OAuthUser). The default is
https://oauth.pstmn.io/v1/callback. -
For Auth URL, enter the OAuth 2.0 authorization endpoint (v2) value from “Endpoints” in the app.
Example:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant_id>/oauth2/v2.0/authorize -
For Access Token URL, enter the access token URL.
Example:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant_id>/oauth2/v2.0/token/ -
For Scope, you must provide “offline_access” as the scope, along with the actual scope. The refresh token is only provided if the offline_access scope was requested.
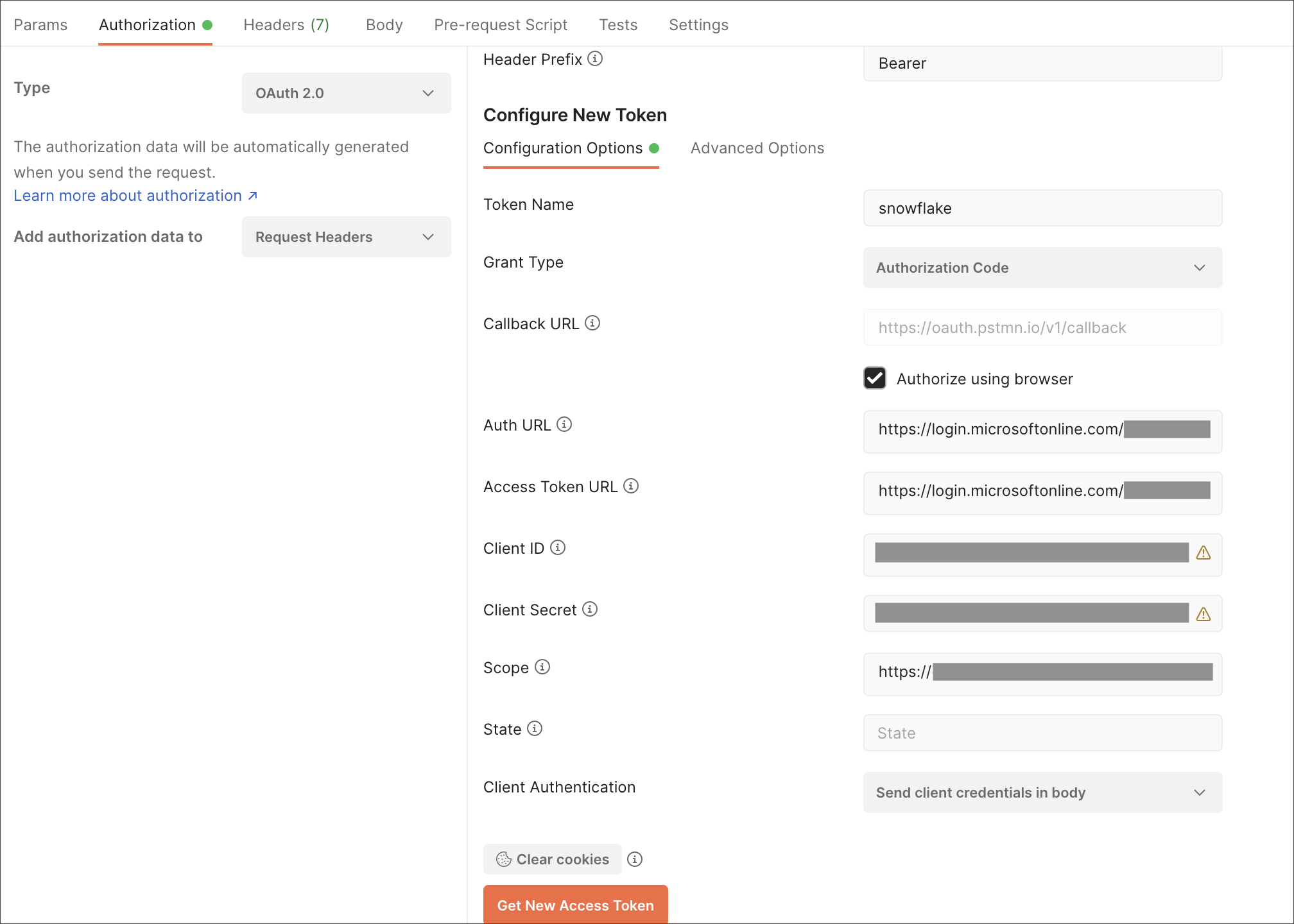
Example:
https://<application_id>/session:role-any offline_accessWhen you create the scope in the Azure AD application setup, it must be set as “any” so that a user can later switch to any of his allowed roles when making a JDBC connection using the obtained token. -
Select Get New Access Token.
-
Sign in to your Microsoft Azure account.
-
On the Token Details page, select Use Token.


-
Verify the validity of the generated access token by running this SQL in Starburst:
select system$verify_external_oauth_token('<access_token>');
Method 2: cURL
To validate your configuration using cURL, do the following:
-
Execute the following command to get access token with password grant_type:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8" \ --data-urlencode "client_id=<OAUTH_CLIENT_ID>" \ --data-urlencode "client_secret=<OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET>" \ --data-urlencode "username=<AZURE_AD_USER>" \ --data-urlencode "password=<AZURE_AD_USER_PASSWORD>" \ --data-urlencode "grant_type=password" \ --data-urlencode "scope=<SCOPE_AS_IT_APPEARS_IN_AZURE_APP>" \ '<AZURE_AD_OAUTH_TOKEN_ENDPOINT>'
Example:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8" \ --data-urlencode "client_id=<client_id>" \ --data-urlencode "client_secret=<client_secret>" \ --data-urlencode "[email protected]" \ --data-urlencode "password=*****" \ --data-urlencode "grant_type=password" \ --data-urlencode "scope=https://<application_id>/session:role-any offline_access"\ `https://login.microsoftonline.com/ <tenant_id>/oauth2/v2.0/token'
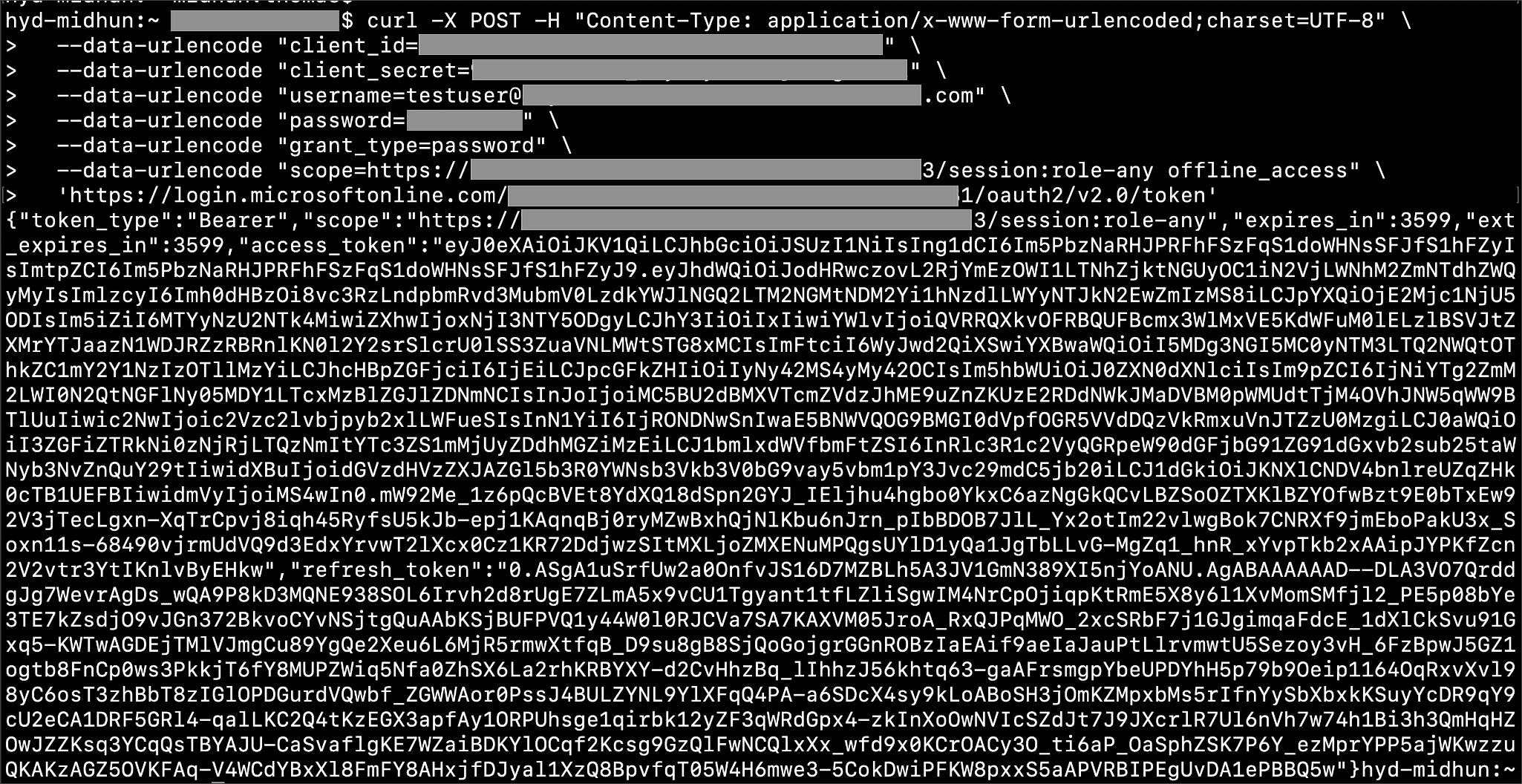
-
Execute the following command for getting access token with refresh_token as grant_type:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8" \ --data-urlencode "client_id=<client_id>" \ --data-urlencode "client_secret=<client_secret>" \ --data-urlencode "grant_type=refresh_token" \ --data-urlencode "refresh_token=<Replace_Refresh_Token>" \ --data-urlencode "scope=https://<application_id>/session:role-any offline_access" \ 'https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant_id>/oauth2/v2.0/token'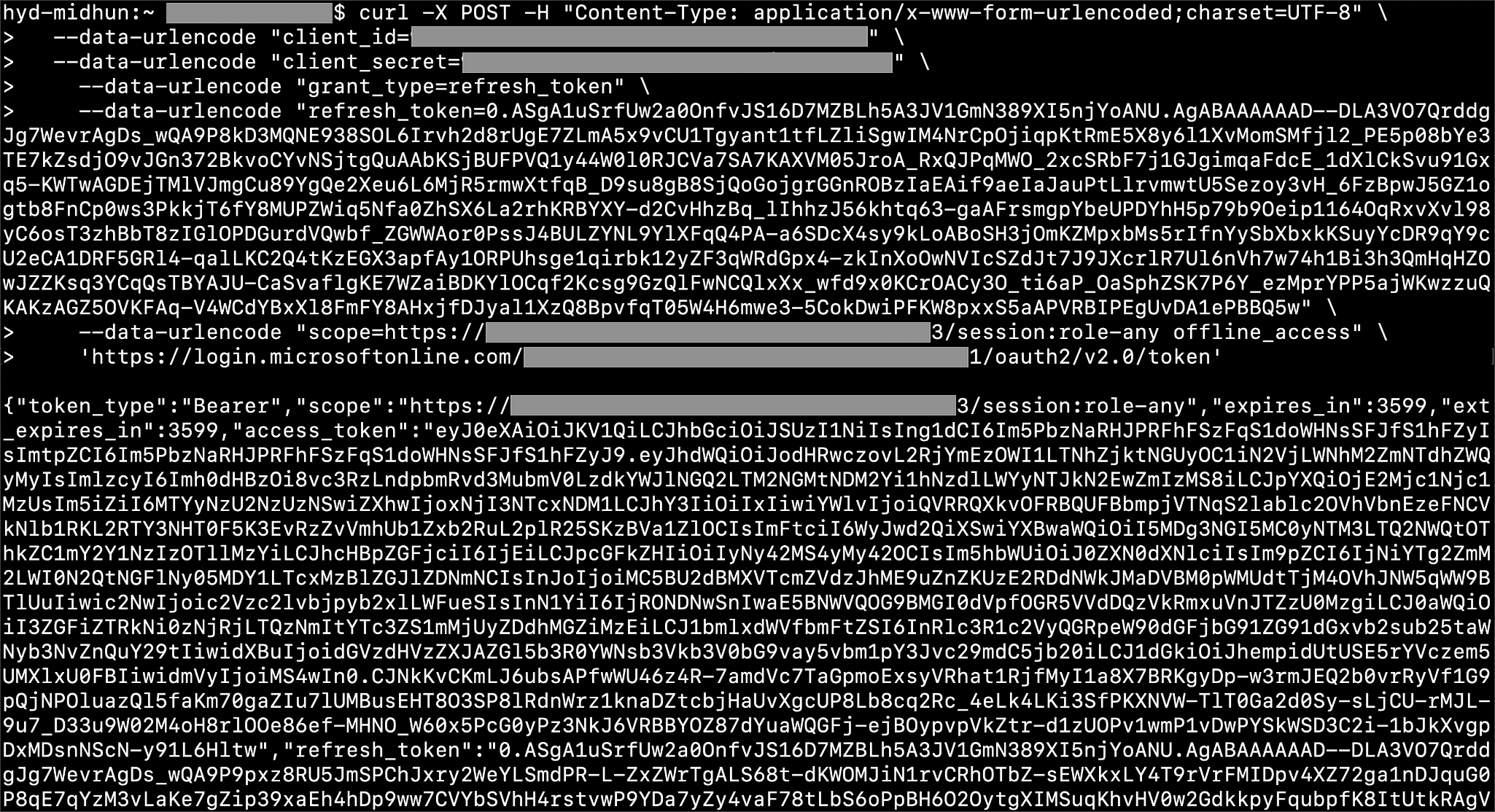
-
Verify the validity of the generated access token by running this SQL in Starburst:
select system$verify_external_oauth_token('<access_token>');
Related information



