Capacity planning for connections
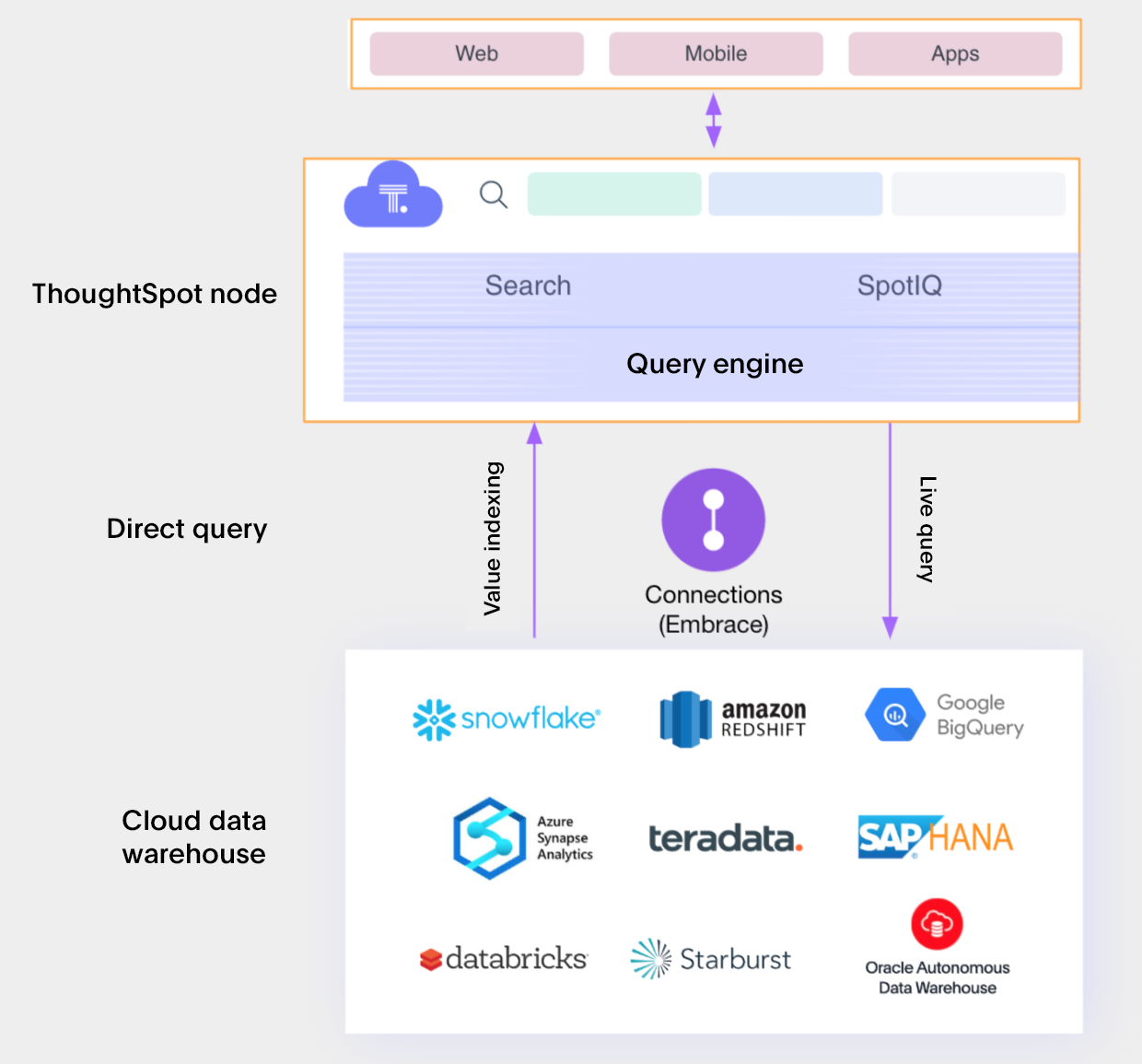
This article provides hardware requirements and recommendations for using connections with ThoughtSpot. Please note that actual hardware requirements will vary depending on many factors like number of users, groups, Worksheets, Liveboards, and more.
These recommendations are only for connections to cloud data warehouses in ThoughtSpot.
ThoughtSpot architecture
Factors influencing capacity
There are numerous factors which affect the capacity required for connections in ThoughtSpot.
Number of concurrent active users
Many sizing exercises begin with a total number of users that the system should be able to handle. For example, a customer needs a system sized for 10,000 users. Once we know the total number of users that will be using the system, the next step is to determine how many of those users will be logged in to the system at the same time during peak period. This can vary widely depending on the geography of user distribution and user personas. To continue with our example, let’s assume at any time, 10% of the total user will be using the system. This will bring peak active users to be 1000. Next we will need to determine the load generated by 1000 active users. This will depend on the activity level of the users in the system. Let’s assume each user is generating 5 requests in 1 min, 1000 users will generate nearly 85 requests per second.
The number of concurrent active users is the number of users actively interacting with ThoughtSpot at any point in time. More concurrent active users mean more requests to the system which require CPU and memory to process.
The number of requests that the system can handle depends on the type of request and metadata in the system. For example, the CPU and memory required to make object metadata create/update calls are higher than object read calls. Similarly, a customer with a large number of users or groups in the order of 50K to 100K may need more resources to process the same request compared to a customer with a simpler setup.
Note that the cloud data warehouse can also limit the total number of requests that a system can handle. Tuning and scaling the cloud data warehouse to meet request-rate requirements is beyond the scope of this documentation.
The general recommendation is that ThoughtSpot can handle 30 concurrent read request/sec with 16 vCPU/128 GB RAM, provided the cloud data warehouse is able to handle the query load.
It is important to understand the usage pattern of the users to figure out the request rate generated by concurrent active users.
Please refer to Scale up/out for more information on how to set up the cluster for a higher request rate. There is no single rule that can help with this calculation, so we recommend that every customer do their own testing to find out the peak load and setup capacity accordingly.
Total number of objects in the system
The ThoughtSpot server caches all the objects and metadata associated with objects in memory so that it can serve user requests with low latency. These cached objects are replicated across all the nodes. During processing of user requests, services might make copies of objects as well. This requires the system to have sufficient memory to store and process objects. The actual amount of memory required depends on the type and complexity of objects in the system. Some examples of objects that take up memory are:
-
Worksheets with a large number of columns
-
Liveboards with many visualizations
-
User groups with a large number of users
-
Overall number of connections, Worksheets, Liveboards, users, groups, and views
In general, ThoughtSpot can hold and serve up to 500K objects in 128GB of RAM.
Number of indexed tokens
-
Manage suggestion indexing provides details of what indexing is and how to control what is indexed or not. Based on the data model and data, customers should be able to get an estimate of the number of tokens that will be indexed.
-
In general, we have seen 500MB of memory/1M token. It is a general recommendation, and actual memory usage will depend on the size of each token.
-
Data tokens are replicated on two nodes in a multi-node cluster so the total memory required to hold indexed data tokens is twice the memory required for holding the total number of tokens in a multi-node cluster.
Disk capacity
ThoughtSpot recommends 800 GB Premium SSD secondary disk and 250GB of Boot Volume per cluster for smooth operation of the cluster. ThoughtSpot uses the secondary disk to store snapshots, customer’s metadata and service logs.
Minimum hardware requirements for production
These are the minimum hardware requirements for a single-node cluster to run a ThoughtSpot application. For a multi-node setup, you can replicate this.
| vCPU | RAM | Premium SSD Managed Disk Volume | Boot Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
16 vCPU |
128 GB RAM |
2 * 400GB |
250 GB |
Scale up/out capability
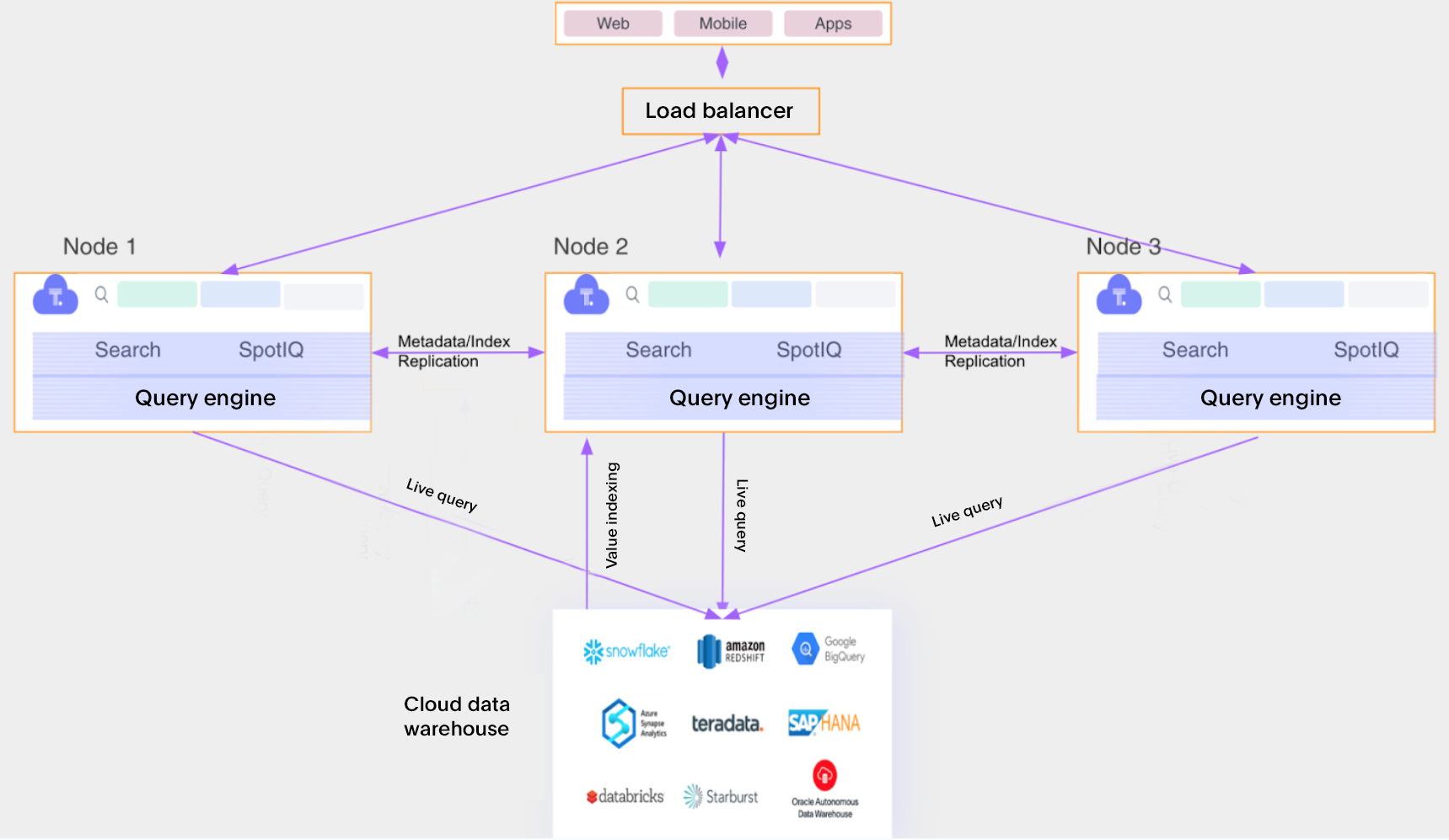
ThoughtSpot is designed to scale up or scale out linearly with request rate. This means that a 2-node cluster can handle twice the number of requests compared to a single-node cluster. Similarly, a single node with 2X CPU and 2Y RAM can also handle twice the number of requests compared to a node with X CPU and Y RAM.
ThoughtSpot replicates all the metadata and objects across all nodes in the cluster, so it does not scale out with increase in metadata size. The only way to fit more metadata in the cluster would be to scale it up by adding more memory to the system.
High Availability
ThoughtSpot is designed to be Highly Available. High Availability setup ensures that the ThoughtSpot application is available to the user in case one node fails. For High Availability setup, we require at least 3 nodes in the cluster.
You can also choose a backup or snapshot strategy to recover from failure. You can learn more about how to set up the backup and snapshot configuration for your cluster in Choose a backup strategy.
Related information