Manage suggestion indexing
When a user searches in the Search bar, ThoughtSpot displays to the user token suggestions for column values. These values are derived from the ThoughtSpot Search index. These indexed values are also displayed in the following components: Column sample values, Explore token suggestions and Spotter value suggestions. Importantly, ThoughtSpot Search Indexing is unrelated to database indexing and query performance.
For tables and views, a column’s INDEX TYPE controls whether and how ThoughtSpot builds the Search Index for each column. For Models, the SUGGEST VALUES IN SEARCH section for a column determines whether ThoughtSpot suggests these indexed column values.
Additionally, ThoughtSpot uses a column’s INDEX PRIORITY value to influence the ranking of the column’s name. These values impact the dynamically calculated usage based ranking (UBR).
| This setting is not applied to the ranking of column values in the search suggestions. |
To configure certain the schedule for ThoughtSpot’s indexing behavior, refer to Managing search and SpotIQ settings.
Building search indexes
Search indexes are built as a background process to index the metadata (column names, synonyms, names, etc.) and optionally the values from the data in your attribute columns. Date columns are not included.
Search indexes are built automatically after an upgrade, and periodically thereafter. Indexes are also rebuilt when you add a new table or column, when adding or changing row-level security rules to a table, and when changing the index type from DONT_INDEX to a different value. Note that you can configure when the index is built, but the default rebuilding schedule is every 24 hours following the last scheduled search index build, or the last unscheduled restart of the search index process.
Data value search indexes are built by running sampling and indexing SQL queries, based on the columns with indexing enabled. For sampling, two SQL queries are generated for each indexed column: one SQL query to get an approximate unique count, and one SQL query to get 1,000 sample values. This helps to determine whether to use prefix only or include word prefixes. These SQL queries are marked with the comment “task: SAGE_SAMPLING”.


For indexing, one SQL query is generated to get all unique values for the column. These SQL queries are marked with the comment “task: SAGE_INDEXING”.

Example of Search suggestion behavior
The following example illustrates how searching for promotion_last_name t causes the system to suggest several ways of completing the t in the search:
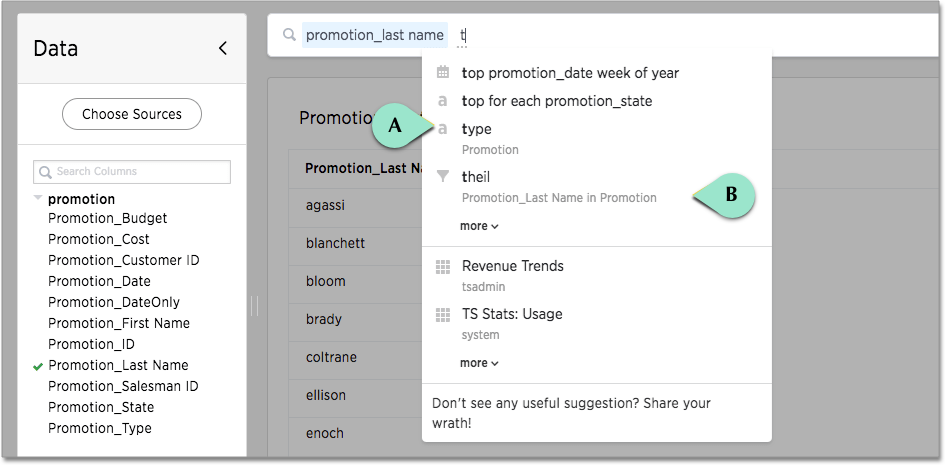
The system is suggesting the synonym type (callout A) for a column in the Promotion table.
It is also suggesting a value of theil (callout B) for the Promotion_Last Name column.
If you look in the page, you can see that there is a type synonym for the Promotion_Type column which is using default indexing.
Without search indexes, you would need to know which column contained which exact value, and specify a filter such as product = ‘andorra ¼ zip jacket’.
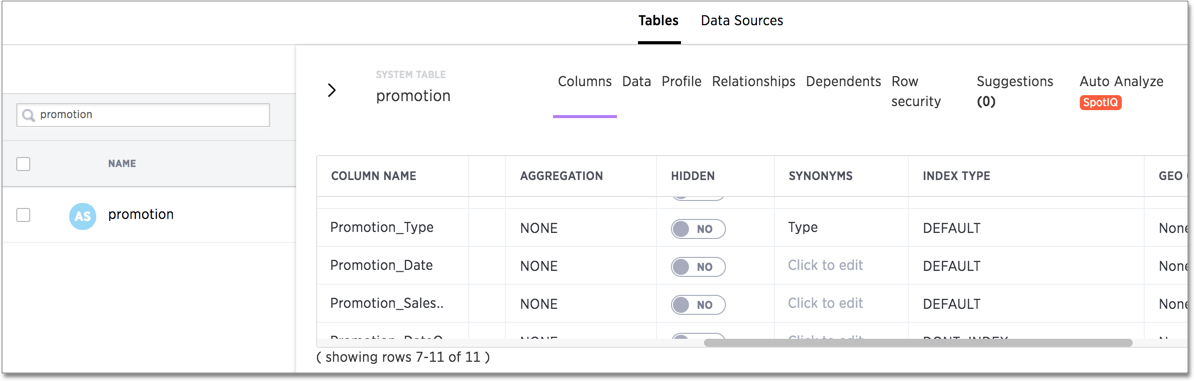
Search indexes suggest the following types of values when users type in the Search bar: column names, synonym names, formula names, column data values, formula data values, and keywords. When using Explore, suggestions are provided for: column filters, adding columns, replacing columns, and comparisons.
Managing search suggestions through INDEX TYPE and INDEX PRIORITY is important. Properly configured suggestions can decrease "noise" in the suggestion list. Increasing the visibility of important columns is helpful for new or intermittent ThoughtSpot users.
Understand the default indexing behavior for tables and views
ThoughtSpot has a system default INDEX TYPE behavior for search suggestions for table and view values. This system default is configured on your cluster and applies to all tables. You can override this default behavior on a per-column basis.
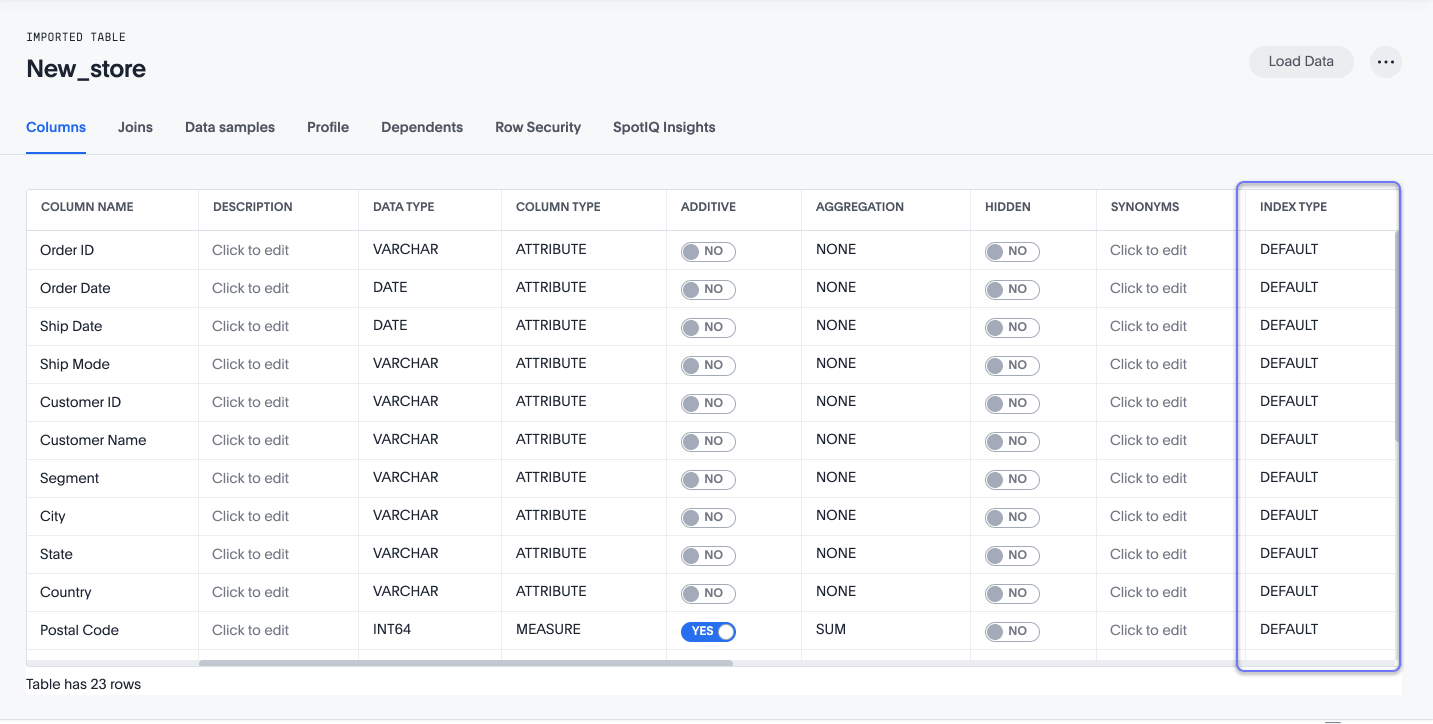
The system behavior when the INDEX TYPE is DEFAULT is as follows:
-
With two exceptions, the system indexes all columns using their COLUMN NAME value. The exceptions are columns with COLUMN TYPE of
MEASUREand columns with DATA TYPE ofDATE. -
Columns that contain data values with large amount of free-form strings, that is, a length greater than 50 words, are indexed as
PREFIX_ONLYby default.If a column has a very large free text value, ThoughtSpot recommends you keep DEFAULTor setDONT_INDEX. Other settings indexing on these values may generate confusing suggestions. -
Short strings (like a
firstnamecolumn) are indexed usingPREFIX_AND_WORD_SUBSTRINGby default, which indexes prefixes for each individual word in the column value. -
If a column has a cardinality - the number of unique column values - greater than 100,000, and the index type is
DEFAULT, ThoughtSpot does not index it. You can index columns with a greater cardinality than 100,000, but it may impact performance. To index a column with a cardinality greater than 100,000, set the index type toPREFIX_ONLY. If you must index a column with high cardinality using a type other thanPREFIX_ONLY, contact ThoughtSpot support.
For column cardinality greater than 10 million and any index type excepting DEFAULT, ThoughtSpot does not index the column.
Understand the indexing behavior for Models
At the Model level, you can choose whether the indexed values are shown or not for a particular column. This is controlled via the SUGGEST VALUES IN SEARCH toggle.
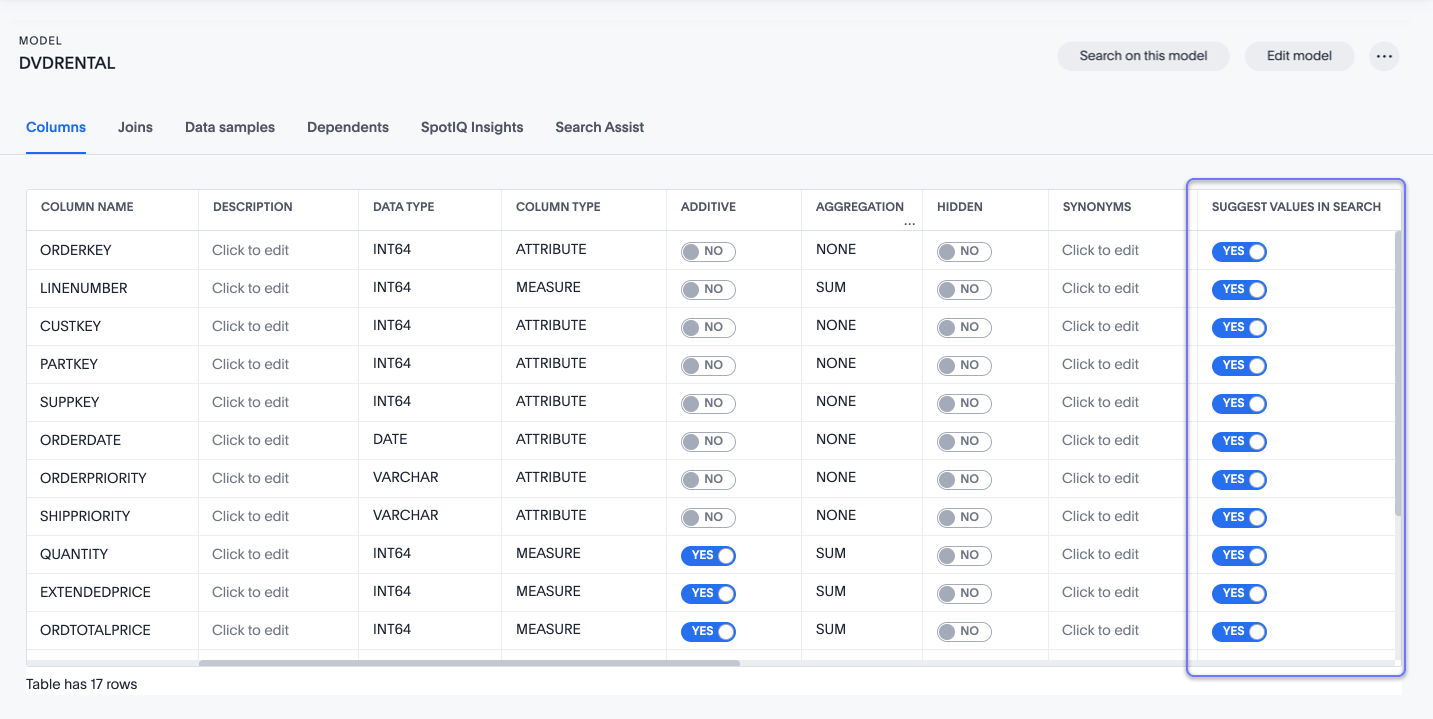
| Indexing only works at the table level. If the underlying table column’s INDEX TYPE is set to 'DONT INDEX', the respective Model column won’t be indexed and be able to 'suggest values'. |
For each non-date attribute formula in a Model, you can control whether data value search suggestions should be provided (toggle to YES to enable a search index of type DEFAULT) and set the formula name index priority.
Turn off indexing for a column
If you don’t want values from a certain column to show up as suggestions in the search bar, it’s simple to turn off indexing for that column.
To turn off indexing for a column:
-
Navigate to the table containing the column you want to prevent from indexing in the Data workspace.
-
Scroll to the Index Type column in the Columns view of the table. Click the Index Type dropdown for the column and select DONT_INDEX.
-
Click Save changes.
Row-level security and indexing
There are two possibilities for row-level security and indexing. If the RLS rule is not supported (that is, it’s valid in SQL, but not when creating indexes), then no index is created. If the RLS rule is supported, then the index will be created as per the RLS rule (at group, user, or a combination of these levels).
High cardinality and performance
A column’s cardinality can impact indexing. If you have a column with a very high cardinality and a very high number of rows, indexing these values can impact your ThoughtSpot performance. ThoughtSpot considers columns with over 100,000 unique values to have high cardinality. ThoughtSpot Support recommends you turn off indexing of primary key columns on extremely large tables (unlimited number of rows but < 100,000 unique values) in your cluster.
High cardinality is relative to other considerations. In some cases, columns with fewer than 100,000 rows but with columns containing long strings can cause performance problems with memory. If you have concerns or questions, your ThoughtSpot contact can help you determine appropriate cardinality thresholds for your ThoughtSpot installation.
To index a column with a cardinality greater than 100,000, set the index type to PREFIX_ONLY, PREFIX_AND_WORD_SUBSTRING, or PREFIX_AND_SUBSTRING. If you must change the cardinality limit for DEFAULT columns, contact ThoughtSpot support.
Configure your own instance defaults
If you need to, you can work with ThoughtSpot support to configure new instance defaults. These include disabling search indexing for your instance, requesting a change to the default frequency of search index builds (every 24 hours), or specifying what time window in which search index builds start.
Additionally, you can configure certain aspects of ThoughtSpot’s indexing behavior from the Admin Console. Refer to Managing search and SpotIQ settings.
To monitor search indexing queries, reference the Index Statistics Liveboard, or the Indexing Queries Liveboard.
Override the system default on a column
You can change a column’s INDEX TYPE in the page or in the Index value in the TML file.
The values you can set for INDEX TYPE are:
| Index type | Description |
|---|---|
DEFAULT |
The default behavior applies to all |
DONT_INDEX |
Prevents indexing on the column values. The column doesn’t appear in search suggestions. |
PREFIX_AND_SUBSTRING |
Allows full indexing such that prefix and sub-string search both work for the column values. |
PREFIX_AND_WORD_SUBSTRING |
Allows indexing such that only prefix search works for each word of a multi-word string, for the column values. |
PREFIX_ONLY |
Allows indexing such that only prefix search works for the column values. |
Consider a column in which there are four values ThoughtSpot, Thought, Spot and Thought Spot.
If you search for sp, depending on the setting for indexing, the column value search result suggestions will vary:
| Index field value | Search bar suggestions |
|---|---|
|
|
|
No suggestions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The DEFAULT behavior is to use PREFIX_AND_SUBSTRING for short values (30 characters or less) and PREFIX_ONLY for long values and free-form text (greater than 50 words).
To change a value in the application UI:
-
Open a Model or table from the Data page.
-
Find the column whose index type you want to modify.
-
Set its INDEX TYPE.
-
Save your changes.
If you are using the TML file, locate the Index cell, and enter the INDEX TYPE you want to use.
Search index suggestion ranking
Column name search suggestions are ordered based on historical usage (UBR- usage-based ranking) and the defined column index priority (1-10). By default, each column has an index priority of 1. This means suggestions that match the names of different columns are all ranked equally. To elevate a column name in the suggestion list, increase the INDEX PRIORITY. This applies a weighting in the underlying algorithm, but does not guarantee a specific column will always be ranked first.
Data value search suggestions are only ordered based on UBR.
Change a column’s suggestion priority
A column’s INDEX PRIORITY determines the order or rank in which it and its values appear in the search suggestions dropdown list. It also affects which columns ThoughtSpot prioritizes when generating AI Answers.
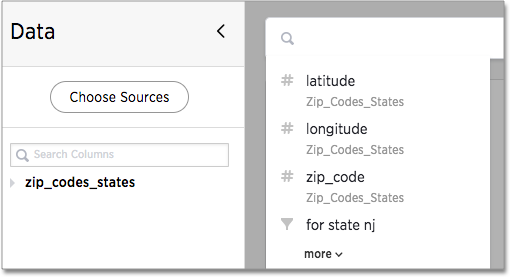
By default, the INDEX PRIORITY value is set to 1 for all columns.
You can push a column up in the order (increase the rank) by increasing its INDEX PRIORITY value.
A higher value (like 2) will cause the corresponding column and its values to appear higher up in the search dropdown list than columns with lower value (like 1).
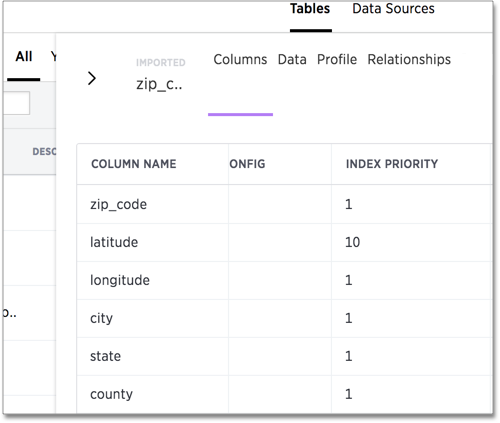
You should only use numbers between 1-10 in the INDEX PRIORITY field. Use a value between 8-10 for important columns to improve their search ranking.
Use 1-3 for low priority columns.
To change a value in the application UI:
-
Open a Model or table from the Data page.
-
Find the column whose index type you want to modify.
-
Change the INDEX PRIORITY to a number between 1 and 10.
-
Save your changes.
If you are using the model file, locate the Index cell, and enter the priority you want to use.
Related information



