Architecture components
To implement ThoughtSpot it is important to understand where it sits within your overall analytics architecture and how it provides data to end users.
ThoughtSpot consists of a cluster of one or more nodes, acting together to provide analytic answers to business questions. As such, there are only a few integration points with ThoughtSpot on your network. The major components in a ThoughtSpot cluster are:
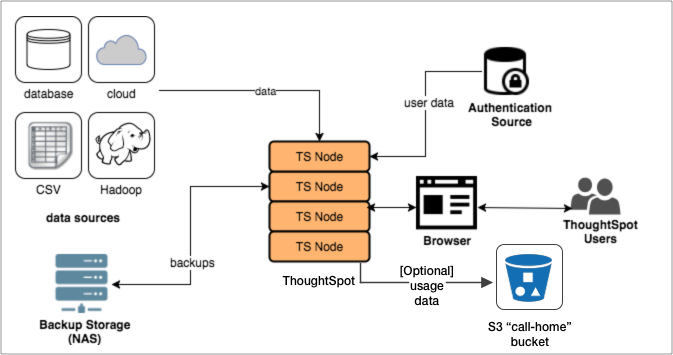
ThoughtSpot can handle a wide variety of different data sources. ThoughtSpot does all analysis against data in memory to help achieve fast results across millions and billions of records of data. ThoughtSpot caches data as relational tables in memory. You can source tables from different data sources and join them together. ThoughtSpot has several approaches for getting data into the cluster.
For cases where your company stores data externally in data warehouses, use Connections to access and query your data. To cache data within ThoughtSpot, you can load it directly using Dataflow, or the tsload command-line tool. JDBC and ODBC drivers are also available. See Data Use Strategies for more information.
The ThoughtSpot appliance can be a physical appliance that ThoughtSpot ships, one or more AWS instances that are clustered together, or one or more VMware instances that are clustered together. From an external interface, regardless of the appliance type, the appliance appears to be a single instance.
For authentication (logging in), some source of user information is required. These define the login requirements and access control groups. Users must access the data from a supported browser to view saved content, or perform search-based analytics. Finally, it is recommended that you have some sort of networked attached storage for storing backups in case of hardware failure.
Related information



